Thomas O'Carroll: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | __NOTOc__[[File:ToC.png|thumb|Thomas O'Carroll]]'''Thomas Victor O'Carroll''' (born c. 1945<ref name="bbc21">[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/england/coventry_warwickshire/5367968.stm "Pair admit to child porn charges,"] September 2006, [[BBC]].</ref>) is an Irish/British journalist, academic and advocate for [[Minor Attracted Person|MAPs]], being an early member and chairperson of the now defunct [[Paedophile Information Exchange]] (PIE), and a founding member of [[Ipce]]. | ||
Born in County Carlow, Ireland<ref | Born in County Carlow, Ireland, O'Carroll gained notoriety in 1980 when he published ''[[Paedophilia: The Radical Case]]''<ref>[http://www.ipce.info/host/radicase/preface.htm Paedophilia: The Radical Case, PDF (hosted on IPCE)]; The same PDF is [http://library.lol/main/A3AE585C3F0C54C3EAB7CDC09EA8C90F archived with novel description on Libgen].</ref>, a book that articulated an ethical case for adult-child sexual relationships, and again in 2010, with ''Michael Jackson's Dangerous Liaisons''.<ref>[https://www.amazon.com/Michael-Jacksons-Dangerous-Liaisons-Carl/dp/1848763409 Amazon: Dangerous Liaisons]</ref><ref>[https://libgen.rocks/ad.php?md5=d1ba0af152fa18c758c3f8cc415a2fd7&uid=1602 Libgen: Dangerous Liaisons]</ref> O'Carroll has also published a number of academic articles. British mainstream media has dubbed O'Carroll both Ireland<ref>[https://www.theguardian.com/media/2003/mar/04/digitaltv.broadcasting Cozens, BBC braced for paedophile row (''The Guardian'', 2003)]</ref> and Britain's "most notorious paedophile".<ref>[https://www.thesun.co.uk/news/8548584/paedophile-tom-ocarroll-invited-to-house-of-lords-bash/ Wilkinson, LOUSE OF LORDS: Vile paedophile campaigner invited to plush champagne bash at the House of Lords (''The Sun'', 2019)]</ref><ref>[https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-8466899/Paedophiles-rebrand-minor-attracted-persons-chilling-online-propaganda-drive.html Denkinson, Outrage as paedophiles rebrand themselves as 'minor-attracted persons' in chilling online propaganda drive (''Daily Mail'', 2019)]</ref> | ||
Gay historian [[William Percy]] stated that O'Carroll argued "''for replacement of the age of consent law with a more flexible and liberal legal framework. It was felt the legitimate protection of children could be reconciled with an acceptance of child sexuality, the right of the young to sexual self-determination, and the legitimacy of consensual child-adult sexual contacts. A journalist, O’Carroll was PIE’s public face in the later 70s, when he propelled the organisation to national prominence''".<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20220403230005/http://www.williamapercy.com/wiki/index.php?title=Category:O%27Carroll,_Tom Percy wiki entry for O'Carroll] (webarchive)</ref> | |||
==Works== | |||
:''For a full list of writings and analysis thereof, see [https://www.boywiki.org/en/Tom_O'Carroll BoyWiki].'' | |||
===Paedophilia: The Radical Case=== | |||
In 1980 O'Carroll's book [[Paedophilia: The Radical Case]] was published and in the preface he states: | |||
:''"I am a paedophile, and in the chapters that follow it will become apparent why I have felt it necessary to crash through the barriers of societal disapproval by speaking out. The fact that I have been able to do so owes much to the work, described in Part Three, of the Paedophile Information Exchange (PIE), a group with which I have been closely connected, which has been campaigning since its inception in 1974 for the open discussion of paedophilia, and for abolition of the laws against consensual sexual acts between children and adults." | |||
Described as "a well researched and articulate book" by Guardian editor Alan Rusbridger (Guardian, 14 March 1981), this first major work by O'Carroll divided reviewers sharply. In the academic world, it has stood the test of time with over 90 Google Scholar citations by 2012. For many years, it was a recommended text for postgraduates at Cambridge University's Institute of Criminology. | |||
===Michael Jackson’s Dangerous Liaisons=== | |||
O’Carroll’s book on singer Michael Jackson was published in 2010 under the pen name “Carl Toms”. Michael Jackson’s Dangerous Liaisons, a 624-page work, essayed a comprehensive review of the late entertainer’s controversially intimate relationships with preadolescent and adolescent boys. Published in the UK by Troubador Publishing Ltd. "At seventeen years in the making and a hefty 624 pages, this has been O'Carroll's most ambitious work, in which, under the pen name Carl Toms, he essays a comprehensive review of the late entertainer’s controversially intimate relationships with young boys. Described in the linked biography by historian [[William Percy]] as "a work of genius", Michael Jackson's Dangerous Liaisons received enthusiastic pre-publication endorsements from five eminent professors, including [[Richard Green]], [[Donald West]], [[James Kincaid]], [[Thomas Hubbard]], and Percy himself. After publication another renowned scholar, J. Michael Bailey, professor of psychology at Northwestern University, also gave high praise in a four-page review for the academic journal [[Archives of Sexual Behavior]]. Bailey, a family man, wrote, “The idea that pedophilic relationships can be harmless or even beneficial to children is disturbing to many people, including me.” But, he continued, “The lack of scientific evidence supporting my largely visceral reactions against pedophilic relationships has been one of the most surprising discoveries of my hopefully ongoing scientific education. [...] O’Carroll argues against my intuitions and he argues well.” | |||
==Television== | |||
O'Carroll has made various appearances on television, including the BBC's ''After Dark'' and Australia's ''60 Minutes''. There is at present no online copy of O'Carroll's ''After Dark'' appearance, while his ''60 Minutes'' is heavily shortened from over an hour, to only short clips online. In 2014, O'Carroll was interviewed for over an hour for "''The Paedophile Next Door''", a film which eventually aired November 25, 2014 on Channel 4 (a U.K. television network). O'Caroll's interview was not used by the director: instead, O'Carroll shared the (unedited) audio online,<ref>[https://soundcloud.com/david-kennerly/stitching-up-steve-humphries A slightly edited version is available online at Soundcloud].</ref> which was turned into an amateur film by one of his readers, titled ''A Decent Life: The Dissenting Narrative of Tom O'Carroll''.<ref>[https://www.boywiki.org/en/A_Decent_Life:_The_Dissenting_Narrative_of_Tom_O%27Carroll_(film) A Decent Life: The Dissenting Narrative of Tom O'Carroll] (Youtube).</ref> | |||
A 2018 full-length and uncensored video discussion/debate between himself and then psychology student Danny Whittaker, can be watched easily on Youtube.<ref>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J8SBM-yXULc #051- Interview with a Pedophile (Tom O'Carroll). 2018 (Youtube).]</ref> | |||
==An often-"cancelled" personality== | |||
[[File:ToCperv.png|thumb|Quote from ''Radical Case'' on non-consent [[paraphilia]]s]] | |||
O'Carroll is no stranger to being courted by prestigious platforms due to his experience in MAP advocacy, but has often subsequently fallen foul of public backlash. For example, in 2001 ''Is paedophilia violent?'', a paper for the ''World Congress of Sexology'', Paris, was given sustained encouragement over nearly a year by Dr Marc Ganem, the Congress President. However, the paper was eventually rejected without explanation by the Committee. After repeated demands for an explanation went unanswered, O'Carroll was finally able to talk to Ganem. In a phone conversation, Ganem indicated that the President of the Scientific Committee, Dr Willy Pasini, appeared to be concerned not about the scientific quality of the paper but by the controversy to which it might give rise. It seems the committee did not want to upset the major pharmaceutical companies sponsoring the congress, nor the politically sensitive [[Wikipedia:World Health Organization|WHO]], with which it was associated. In order to combat this censorship, O'Carroll's supporters attended the congress, where they distributed his paper on a CD, along with a flyer titled ''Censored: The Speech They Didn't Want You To Hear''.<ref>[https://www.helping-people.info/articles/violent_frame.htm ''Is Paedophilia Violent?'' A paper prepared for the World Congress of Sexology, Paris 2001]</ref> | |||
In 2023, O'Carroll detailed how his work for academic publishers had generated a rash of attention, following the retraction of his peer-reviewed and published book chapter from the IntechOpen book ''Ethics in Scientific Research: New Perspectives''. Retracted without explanation and likely on the basis of his open [[MAP]] identity, O'Carroll identified a group of radical [[Feminism|Feminists]] attached to the ''Sexnet'' private forum as the likely cause. His chapter was entitled "''Where Angels Fear to Tread: Anxieties over Researching Child Sexuality Must Be Overcome''", and can be read elsewhere online.<ref>[https://heretictoc.com/2023/08/17/from-fallen-angels-to-bare-bear/ From fallen ‘angels’ to bare Bear], re. [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369197385_Where_Angels_Fear_to_Tread_Anxieties_over_Researching_Child_Sexuality_Must_Be_Overcome Where Angels Fear to Tread: Anxieties over Researching Child Sexuality Must Be Overcome (2023 book chapter)]</ref> | |||
==Run-ins with the law== | ==Run-ins with the law== | ||
In 1981 | In 1981, O'Carroll was convicted for the archaic and rarely prosecuted political crime of "conspiracy to corrupt public morals", over the contact ads section of the PIE magazine and was imprisoned. He had some defenders in the press, and [[The Campaign Against Public Morals]] (CAPM) was formed in his defence, producing a [[Communism|left-wing]] booklet entitled "''Paedophilia and Public Morals''" (1980) which scrutinized patriarchal, state and family oppression of young people, as well as defending the indicted PIE committee members. O'Carroll was once again imprisoned much later in 2002, on charges of evading a prohibition on the importation of [[Child porn|indecent photographs of children]] stemming from nude photographs that O'Carroll had taken of children on the beaches of Qatar. At the time, he was working on a book about the musician and philanthropist Michael Jackson who was later acquitted of charges brought against him regarding indecent behavior towards a child. | ||
Later, O'Carroll was arrested | Later, O'Carroll was arrested on suspicion of conspiring to distribute indecent photographs of children after supplying an undercover [[Metropolitan Police|Met]] police officer (who over a three year period gained O'Carroll's trust) with a cache of [[child pornography]] obtained from his co defendant, Michael John De Clare Studdert's collection. He was arraigned 1 June, 2006 on child porn charges.<ref name="bbc21" /><ref>[http://www.thisisthenortheast.co.uk/display.var.779431.0.police_charge_man_over_child_sex_ring.php "Police charge man over child sex ring"], by Olivia Richwald, ''[[The Northern Echo]]'', 1 June 2006</ref> In September 2006, he was charged with two counts of distributing indecent images of children.<ref name="bbc21" /> | ||
On December 20 2006, he was jailed for 2½ years at London’s Middlesex Crown Court,<ref name=beebgaol>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/england/coventry_warwickshire/6196811.stm BBC NEWS | UK | England | Coventry/Warwickshire | Two jailed for child porn library<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> | On December 20 2006, he was jailed for 2½ years at London’s Middlesex Crown Court,<ref name=beebgaol>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/england/coventry_warwickshire/6196811.stm BBC NEWS | UK | England | Coventry/Warwickshire | Two jailed for child porn library<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> but was released in the summer of 2007. This case was described as a “sting operation”.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20190330235201/http://www.williamapercy.com/wiki/index.php?title=Tom_O%27Carroll_Biography Tom O'Carroll Biography]</ref> | ||
= | |||
< | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 43: | ||
*[https://heretictoc.com/ Personal Blog] | *[https://heretictoc.com/ Personal Blog] | ||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20080724183953/http://www.inquisition21.com/article~view~69~page_num~11.html "Reflections on Thomas O'Carroll"] | *[https://web.archive.org/web/20080724183953/http://www.inquisition21.com/article~view~69~page_num~11.html "Reflections on Thomas O'Carroll"] | ||
*[http://www.ipce.info/host/radicase/preface.htm ''Paedophilia: The Radical Case''] | *[http://www.ipce.info/host/radicase/preface.htm ''Paedophilia: The Radical Case''] - Also available via [http://library.lol/main/A3AE585C3F0C54C3EAB7CDC09EA8C90F Libgen]. | ||
*[https://libgen.rocks/ad.php?md5=d1ba0af152fa18c758c3f8cc415a2fd7&uid=1602 ''Dangerous Liaisons''], see also an [https://ia902604.us.archive.org/18/items/michael-jacksons-dangerous-liaisons/Michael%20Jackson%27s%20Dangerous%20Liaisons_%20Arvi%20-%20Carl%20Toms.pdf IA Backup]. | |||
*[https://www.boywiki.org/en/A_Decent_Life:_The_Dissenting_Narrative_of_Tom_O%27Carroll_(film) A Decent Life: The Dissenting Narrative of Tom O'Carroll (film)] | |||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20130425190322/http://snifferdogonline.com/reports/Child%20Abuse,%20Sexuality%20and%20Violence/Tom%20Carroll%20Sexual%20Privacy%20Background%20Paper.pdf Sexual privacy for paedophiles and children: a complementary background paper.] By Tom O'Carroll | |||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Official Encyclopedia]][[Category:People]][[Category:People: Sympathetic Activists]][[Category:Law/Crime]][[Category:Law/Crime: British]][[Category:History & Events: Real Crime]][[Category:People: Irish]][[Category:People: Adult or Minor sexually attracted to or involved with the other]] | [[Category:Official Encyclopedia]][[Category:People]][[Category:People: Sympathetic Activists]][[Category:Law/Crime]][[Category:Law/Crime: British]][[Category:History & Events: Real Crime]][[Category:People: Irish]][[Category:People: British]][[Category:People: Adult or Minor sexually attracted to or involved with the other]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:25, 24 August 2024

Thomas Victor O'Carroll (born c. 1945[1]) is an Irish/British journalist, academic and advocate for MAPs, being an early member and chairperson of the now defunct Paedophile Information Exchange (PIE), and a founding member of Ipce.
Born in County Carlow, Ireland, O'Carroll gained notoriety in 1980 when he published Paedophilia: The Radical Case[2], a book that articulated an ethical case for adult-child sexual relationships, and again in 2010, with Michael Jackson's Dangerous Liaisons.[3][4] O'Carroll has also published a number of academic articles. British mainstream media has dubbed O'Carroll both Ireland[5] and Britain's "most notorious paedophile".[6][7]
Gay historian William Percy stated that O'Carroll argued "for replacement of the age of consent law with a more flexible and liberal legal framework. It was felt the legitimate protection of children could be reconciled with an acceptance of child sexuality, the right of the young to sexual self-determination, and the legitimacy of consensual child-adult sexual contacts. A journalist, O’Carroll was PIE’s public face in the later 70s, when he propelled the organisation to national prominence".[8]
Works
- For a full list of writings and analysis thereof, see BoyWiki.
Paedophilia: The Radical Case
In 1980 O'Carroll's book Paedophilia: The Radical Case was published and in the preface he states:
- "I am a paedophile, and in the chapters that follow it will become apparent why I have felt it necessary to crash through the barriers of societal disapproval by speaking out. The fact that I have been able to do so owes much to the work, described in Part Three, of the Paedophile Information Exchange (PIE), a group with which I have been closely connected, which has been campaigning since its inception in 1974 for the open discussion of paedophilia, and for abolition of the laws against consensual sexual acts between children and adults."
Described as "a well researched and articulate book" by Guardian editor Alan Rusbridger (Guardian, 14 March 1981), this first major work by O'Carroll divided reviewers sharply. In the academic world, it has stood the test of time with over 90 Google Scholar citations by 2012. For many years, it was a recommended text for postgraduates at Cambridge University's Institute of Criminology.
Michael Jackson’s Dangerous Liaisons
O’Carroll’s book on singer Michael Jackson was published in 2010 under the pen name “Carl Toms”. Michael Jackson’s Dangerous Liaisons, a 624-page work, essayed a comprehensive review of the late entertainer’s controversially intimate relationships with preadolescent and adolescent boys. Published in the UK by Troubador Publishing Ltd. "At seventeen years in the making and a hefty 624 pages, this has been O'Carroll's most ambitious work, in which, under the pen name Carl Toms, he essays a comprehensive review of the late entertainer’s controversially intimate relationships with young boys. Described in the linked biography by historian William Percy as "a work of genius", Michael Jackson's Dangerous Liaisons received enthusiastic pre-publication endorsements from five eminent professors, including Richard Green, Donald West, James Kincaid, Thomas Hubbard, and Percy himself. After publication another renowned scholar, J. Michael Bailey, professor of psychology at Northwestern University, also gave high praise in a four-page review for the academic journal Archives of Sexual Behavior. Bailey, a family man, wrote, “The idea that pedophilic relationships can be harmless or even beneficial to children is disturbing to many people, including me.” But, he continued, “The lack of scientific evidence supporting my largely visceral reactions against pedophilic relationships has been one of the most surprising discoveries of my hopefully ongoing scientific education. [...] O’Carroll argues against my intuitions and he argues well.”
Television
O'Carroll has made various appearances on television, including the BBC's After Dark and Australia's 60 Minutes. There is at present no online copy of O'Carroll's After Dark appearance, while his 60 Minutes is heavily shortened from over an hour, to only short clips online. In 2014, O'Carroll was interviewed for over an hour for "The Paedophile Next Door", a film which eventually aired November 25, 2014 on Channel 4 (a U.K. television network). O'Caroll's interview was not used by the director: instead, O'Carroll shared the (unedited) audio online,[9] which was turned into an amateur film by one of his readers, titled A Decent Life: The Dissenting Narrative of Tom O'Carroll.[10]
A 2018 full-length and uncensored video discussion/debate between himself and then psychology student Danny Whittaker, can be watched easily on Youtube.[11]
An often-"cancelled" personality
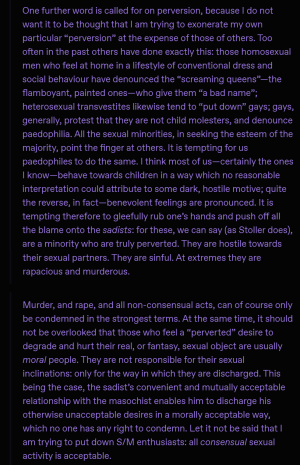
O'Carroll is no stranger to being courted by prestigious platforms due to his experience in MAP advocacy, but has often subsequently fallen foul of public backlash. For example, in 2001 Is paedophilia violent?, a paper for the World Congress of Sexology, Paris, was given sustained encouragement over nearly a year by Dr Marc Ganem, the Congress President. However, the paper was eventually rejected without explanation by the Committee. After repeated demands for an explanation went unanswered, O'Carroll was finally able to talk to Ganem. In a phone conversation, Ganem indicated that the President of the Scientific Committee, Dr Willy Pasini, appeared to be concerned not about the scientific quality of the paper but by the controversy to which it might give rise. It seems the committee did not want to upset the major pharmaceutical companies sponsoring the congress, nor the politically sensitive WHO, with which it was associated. In order to combat this censorship, O'Carroll's supporters attended the congress, where they distributed his paper on a CD, along with a flyer titled Censored: The Speech They Didn't Want You To Hear.[12]
In 2023, O'Carroll detailed how his work for academic publishers had generated a rash of attention, following the retraction of his peer-reviewed and published book chapter from the IntechOpen book Ethics in Scientific Research: New Perspectives. Retracted without explanation and likely on the basis of his open MAP identity, O'Carroll identified a group of radical Feminists attached to the Sexnet private forum as the likely cause. His chapter was entitled "Where Angels Fear to Tread: Anxieties over Researching Child Sexuality Must Be Overcome", and can be read elsewhere online.[13]
Run-ins with the law
In 1981, O'Carroll was convicted for the archaic and rarely prosecuted political crime of "conspiracy to corrupt public morals", over the contact ads section of the PIE magazine and was imprisoned. He had some defenders in the press, and The Campaign Against Public Morals (CAPM) was formed in his defence, producing a left-wing booklet entitled "Paedophilia and Public Morals" (1980) which scrutinized patriarchal, state and family oppression of young people, as well as defending the indicted PIE committee members. O'Carroll was once again imprisoned much later in 2002, on charges of evading a prohibition on the importation of indecent photographs of children stemming from nude photographs that O'Carroll had taken of children on the beaches of Qatar. At the time, he was working on a book about the musician and philanthropist Michael Jackson who was later acquitted of charges brought against him regarding indecent behavior towards a child.
Later, O'Carroll was arrested on suspicion of conspiring to distribute indecent photographs of children after supplying an undercover Met police officer (who over a three year period gained O'Carroll's trust) with a cache of child pornography obtained from his co defendant, Michael John De Clare Studdert's collection. He was arraigned 1 June, 2006 on child porn charges.[1][14] In September 2006, he was charged with two counts of distributing indecent images of children.[1]
On December 20 2006, he was jailed for 2½ years at London’s Middlesex Crown Court,[15] but was released in the summer of 2007. This case was described as a “sting operation”.[16]
External links
- Wikipedia
- Personal Blog
- "Reflections on Thomas O'Carroll"
- Paedophilia: The Radical Case - Also available via Libgen.
- Dangerous Liaisons, see also an IA Backup.
- A Decent Life: The Dissenting Narrative of Tom O'Carroll (film)
- Sexual privacy for paedophiles and children: a complementary background paper. By Tom O'Carroll
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Pair admit to child porn charges," September 2006, BBC.
- ↑ Paedophilia: The Radical Case, PDF (hosted on IPCE); The same PDF is archived with novel description on Libgen.
- ↑ Amazon: Dangerous Liaisons
- ↑ Libgen: Dangerous Liaisons
- ↑ Cozens, BBC braced for paedophile row (The Guardian, 2003)
- ↑ Wilkinson, LOUSE OF LORDS: Vile paedophile campaigner invited to plush champagne bash at the House of Lords (The Sun, 2019)
- ↑ Denkinson, Outrage as paedophiles rebrand themselves as 'minor-attracted persons' in chilling online propaganda drive (Daily Mail, 2019)
- ↑ Percy wiki entry for O'Carroll (webarchive)
- ↑ A slightly edited version is available online at Soundcloud.
- ↑ A Decent Life: The Dissenting Narrative of Tom O'Carroll (Youtube).
- ↑ #051- Interview with a Pedophile (Tom O'Carroll). 2018 (Youtube).
- ↑ Is Paedophilia Violent? A paper prepared for the World Congress of Sexology, Paris 2001
- ↑ From fallen ‘angels’ to bare Bear, re. Where Angels Fear to Tread: Anxieties over Researching Child Sexuality Must Be Overcome (2023 book chapter)
- ↑ "Police charge man over child sex ring", by Olivia Richwald, The Northern Echo, 1 June 2006
- ↑ BBC NEWS | UK | England | Coventry/Warwickshire | Two jailed for child porn library
- ↑ Tom O'Carroll Biography