Research: Youth sexuality: Difference between revisions
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
*'''Clellan S. Ford and Frank A. Beach (1951) [https://libgen.is/book/index.php?md5=EDFEA6F931F7829028850C4ADCF1356E Patterns of Sexual Behavior]. ''New York: Harper and Row''''' | *'''Clellan S. Ford and Frank A. Beach (1951) [https://libgen.is/book/index.php?md5=EDFEA6F931F7829028850C4ADCF1356E Patterns of Sexual Behavior]. ''New York: Harper and Row''''' | ||
*: In their examination of 191 cultures, Clellan S. Ford and Frank A. Beach concluded that as “long as the adult members of a society permit them to do so, immature males and females engage in practically every type of sexual behavior found in grown men and women.” | *: In their examination of 191 cultures, Clellan S. Ford and Frank A. Beach concluded that as “long as the adult members of a society permit them to do so, immature males and females engage in practically every type of sexual behavior found in grown men and women.” | ||
*'''Bhugra, D. (2000). [https://sci-hub.ru/10.1080/14681990050001574 Disturbances in objects of desire: Cross-cultural issues.] Sexual and Relationship Therapy, 15(1), 67–78. doi:10.1080/14681990050001574''' | |||
*:"In their cross-cultural study of the sexual thoughts of children, [https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED224562.pdf Goldman and Goldman (1982)] found that 50% of boys [Editor: actually 5%, not 50%, check in the original paper, p.188] and 9.5% of girls expressed aversion to their biological sex. This reaction peaked in adolescence, with 30% of 13-year-old boys in Australia and 20% in the USA expressing such feelings which, by contrast, were virtually absent in Sweden. Bancroft (1989) suggests that the more rigid the sex role stereotypes in a society, the greater the likelihood of this gender dysphoria. Thus, rigid expectations could produce anxiety and insecurity about gender identity, for which transsexual ideas would offer one method of coping." | |||
==== Factors of earlier sexual development ==== | |||
There is an assumption that cultural sexual restrictions are responsible for the timing of sexual development. While this may be true at some point, there are many other powerful factors that influence timing. | |||
*'''Ellis, B. J., & Essex, M. J. (2007). [https://sci-hub.ru/10.2307/4620739 Family environments, adrenarche and sexual maturation: A longitudinal test of a life history model]. Child Development, 78, 1799–1817.''' | |||
*:"Higher quality parental investment (from both mothers and fathers) and less father-reported Marital Conflict/Depression forecast later adrenarche. Older age at menarche in mothers, higher socioeconomic status, greater mother-based Parental Supportiveness, and lower third-grade body mass index each uniquely and significantly predicted later sexual development in daughters. Consistent with a life history perspective, quality of parental investment emerged as a central feature of the proximal family environment in relation to pubertal timing." | |||
*'''Ellis, B. J., Figueredo, A. J., Brumbach, B. H., & Schlomer, G. L. (2009). [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269820233_Fundamental_Dimensions_of_Environmental_Risk_The_Impact_of_Harsh_versus_Unpredictable_Environments_on_the_Evolution_and_Development_of_Life_History_Strategies The impact of harsh versus unpredictable environments on the evolution and development of life history strategies.] Human Nature, 20, 204–268.''' | |||
*:"The theory posits that clusters of correlated LH [life history] traits (e.g., timing of puberty, age at sexual debut and first birth, parental investment strategies) lie on a slow-to-fast continuum; that harshness (externally caused levels of morbidity-mortality) and unpredictability (spatial-temporal variation in harshness) are the most fundamental environmental influences on the evolution and development of LH strategies; and that these influences depend on population densities and related levels of intraspecific competition and resource scarcity, on age schedules of mortality, on the sensitivity of morbidity-mortality to the organism's resource-allocation decisions, and on the extent to which environmental fluctuations affect individuals versus populations over short versus long timescales. | |||
*'''Del Giudice M. (2014) [https://iris.unito.it/retrieve/handle/2318/1853338/974935/DelGiudice_2018_middle-childhood_chapter_pre.pdf Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.]; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543707/ Handbook of Life Course Health Development]. ''Cham (CH): Springer''; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3''' | |||
*:"In a nutshell, dangerous and unpredictable environments tend to favor fast strategies characterized by early reproduction, sexual promiscuity, unstable relationships, impulsivity, risk taking, aggression, and exploitative tendencies, whereas safe and predictable environments tend to entrain slow strategies characterized by late reproduction, stable relationships, high selfcontrol, aversion to risk, and prosociality. Slow strategies are also favored by nutritional scarcity when danger is low (see Del Giudice et al., 2016; Ellis et al., 2009)" | |||
*:"Another recent example is the finding that early adrenarche is associated with reduced white matter volume in the frontal lobe of children (Klauser et al., 2015). Again, the standard interpretation is that early DHEA exposure has a disruptive effect on neurodevelopmenal processes; however, it is also possible that different trajectories of brain development — and even associated “symptoms” such as anxiety and aggressive behaviors — may instead reflect alternative strategies on a fast-slow continuum of life history variation. Ellis and colleagues (2012) present an extended analysis of adolescent risk-taking from this perspective, and discuss several implications for the design of interventions." | |||
==Early and middle childhood== | ==Early and middle childhood== | ||
| Line 129: | Line 144: | ||
*:"Fetishistic attractions also tend to form in middle childhood, with the onset of pleasurable sensations toward the object of the fetish (e.g., rubber, shoes) that later become fully eroticized (Lawrence, 2009). The onset of fetishistic attractions is part of a generalized awakening of sexuality in middle childhood (Table 1) and illustrates the potential for rapid plasticity with long-lasting outcomes." | *:"Fetishistic attractions also tend to form in middle childhood, with the onset of pleasurable sensations toward the object of the fetish (e.g., rubber, shoes) that later become fully eroticized (Lawrence, 2009). The onset of fetishistic attractions is part of a generalized awakening of sexuality in middle childhood (Table 1) and illustrates the potential for rapid plasticity with long-lasting outcomes." | ||
*:"While learning and play are relatively risk-free, they are not without consequences. The social position achieved in middle childhood is a springboard for adolescence and adulthood; popularity and centrality within the peer network put a child at a considerable advantage, with potentially long-term effects on mating and reproductive success (Del Giudice et al., 2009)." | *:"While learning and play are relatively risk-free, they are not without consequences. The social position achieved in middle childhood is a springboard for adolescence and adulthood; popularity and centrality within the peer network put a child at a considerable advantage, with potentially long-term effects on mating and reproductive success (Del Giudice et al., 2009)." | ||
*: | |||
*:" | * '''[[Gilbert Herdt]] and Martha McClintock, Ph.D, [https://www.ipce.info/sites/ipce.info/files/biblio_attachments/herdt_-_the_magical_age_of_10_2000.pdf The Magical Age of 10], ''Archives of Sexual Behavior'', Vol. 29, No. 6, 2000.''' | ||
*:" | *:"Middle childhood should no longer be viewed as a period of hormonal quiescence. Nor should we believe that for all children, there is an absence of sexual subjectivity before gonadarche. Rather, the accumulating evidence suggests that there is more sexual subjectivity occurring during childhood than previously believed, especially from the age of 6 onward, with the onset of adrenarche." | ||
*:"It is tempting to argue that if attraction typically develops during adrenarche but is ignored or repressed by adults’ retrospection about sexual development, particularly before it becomes stabilized around the age of 10, the contemporary United States may be a good example of a society in which discontinuity in sexuality is a common developmental experience, and may affect the memory of earliest sexual attraction (Herdt, 1990). Because male and female, as well as homosexual and heterosexual experiences of attraction were found before the age of 10, the internal representation of sexual attraction is robust and memorable enough to overcome these societal constraints (McClintock and Herdt, 1996)." | |||
==Fetal/infant sexual capacity== | ==Fetal/infant sexual capacity== | ||
| Line 166: | Line 182: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
*[[Floyd Martinson]] - a pioneer in child sexuality research, contributing more to that field than anyone else in his lifetime | *'''[[Floyd Martinson]]''' - a pioneer in child sexuality research, contributing more to that field than anyone else in his lifetime | ||
*:*Floyd M. Martinson, '''"[https://www.ipce.info/booksreborn/martinson/infant/index.html Infant and Child Sexuality: A Sociological Perspective]"''', ''The Book Mark'', USA, 1973. | |||
*:* Floyd M. Martinson. (1974) '''[https://www.ipce.info/booksreborn/martinson/adolescent/Adolescent.html The Quality of Adolescent Sexual Experiences]'''. ''The Book Mark'' | |||
*:*Martinson, Floyd M. (1981). “'''[http://library.lol/main/1EEA84D225F59C0B4853B57D604F82BB The Sex Education of Young Children]'''”, in ''Sex Education in the Eighties The Challenge of Healthy Sexual Evolution'', ed. by Lorna Brown (Plenum Press: New York), pp. 51-82. | |||
*:*Floyd M. Martinson. '''"[https://libgen.is/book/index.php?md5=16ABA69C5A0F45E04E97BD31A7CD26BE The Sexual Life of Children]"''', ''Bergin & Garvey'', 1994 | |||
*'''[[John Bancroft]]''' - a sexologist, former director in Kinsey's Institute who made great contribution into child and adolescence sexuality | |||
*:*John Bancroft, June Machover Reinisch (1990) '''[https://libgen.is/book/index.php?md5=F212BDB2C84220A1D4E56106B9AD8A6A Adolescence and Puberty]'''. ''Oxford University Press'' | |||
*:*John Bancroft (2003) '''[https://libgen.is/book/index.php?md5=C3F0A409AC9F1193E0BA75B847BC19E4 Sexual Development in Childhood] (Kinsey Institute Series)''' ''Indiana University Press'' | |||
==Excerpt Graphic Library== | ==Excerpt Graphic Library== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:00, 19 November 2024
 | ||||||||||||
| Part of NewgonWiki's research project | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| Template: Research - This template |
Sexual activities among youth under 18 are common and do not tend to damage participants directly. In localities where an association has been seen to exist, socially conservative attitudes and inadequate education, particularly concerning feminine gender roles, are the likely causes.[1] Whilst these experiences play an important part in learning, their diversity challenges the common myth of a uniform "childhood sexuality" characterized by "innocent sex play". Evidence of young people's sexual behavior comes from a variety of sources (see below), including research from anthropology as shown in our page on non-western cultures.
Age-appropriate chronophilia?
It is supposed that as a child develops into an adult, his or her age-preference adjusts naturally in line with his or her age. This corresponding age attraction argument is easily dismissed as ethnocentric to Western cultures, in which children are sorted into same-age peer groups. It is not supported by the evidence.
Sexual behaviour among youth
Effects and perception
The idea of "children" as "perpetrators of sexual abuse" is an American Imperialist worldview originating in the 1980s, as youth sexuality was further problematized. By the 1990s, it had come to predominate in European countries - even formerly liberal Denmark.[2] Our excerpts look mainly at studies that were not conducted under the presumption of abuse.
- Corpuz, R., Kotov, D. A., & Donovan, R. L. (2023) Earlier sexual debut predicts higher (not lower) levels of father care measured across twelve weeks: An experience sampling study. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1199735. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1199735
- “They reported on ages of sexual debut, thorarche [age of first ejaculation], and the years between thorarche and first reproduction (i.e., current age) was calculated. Only age of sexual debut had a relationship with time allocated toward infants. Importantly however, this small effect was in a direction opposite of our LHT derived hypothesis. Males with earlier sexual debut spent more time with their infants.“
- McKee, Alan (2010). Does pornography harm young people? Australian Journal of Communication, 37(1), pp. 17-36.
- "[...]longitudinal research and retrospective studies have consistently shown that similar-aged, consensual sexual experiences among children have no impact on adult sexual adjustment, either positive or negative (Greenwald and Leitenberg, 1989; Kilpatrick, 1992; Okami et al, 1997, p. 340). Lamb and Coakley’s research with adults who recalled childhood sexual games noted that: ‘Statistical analysis showed that these subjects did not differ from those who did not remember any childhood sexual games’ (Lamb and Coakley, 1993, p. 520).
- "It is important that we distinguish between normal childhood sexual play and sexual abuse, and not simply collapse the two of them together (Lamb and Coakley, 1993). As noted above, an extensive tradition of research over many decades has established that sexual play – including looking at naked bodies, or pictures of naked bodies – can be a normal, healthy part of children’s development. But any form of coerced sexual practice – including being forced to look at pornography – can be destructive."
- Yin Xu, Sam Norton & Qazi Rahman (2021). "Adolescent Sexual Behavior Patterns, Mental Health, and Early Life Adversities in a British Birth Cohort". The Journal of Sex Research, 59(1):1-12.
- "This study tested adolescent sexual behavior patterns at age 14, their association with mental health at age 17 (psychological well-being, substance use, and self-harm attempts), and the influence of early life adversities upon this association. A British birth cohort (5,593 boys and 5,724 girls from the Millennium Cohort Study) was used. Latent class analysis suggested five subgroups of adolescent sexual behaviors: a “no sexual behavior” (50.74%), a “kisser” (39.92%), a “touching under clothes” (4.71%), a “genital touching” (2.64%), and an “all sexual activities” class (1.99%). Adolescents from the “kisser,” “touching under clothes,” “genital touching,” and “all sexual activities” classes reported significantly more substance use and self-harm attempts compared to adolescents from the “no sexual behavior” group. The associations became weaker after controlling for early life adversities (reducing around 4.38% to 37.35% for boys, and 9.29% to 52.56% for girls), and reduced to a smaller degree after further controlling for mental health variables at 14. The associations between sexual behaviors and psychological well-being became nonsignificant after controlling for early life adversities. Adolescents who have engaged in low-intensity sexual activities at early age may have poorer reported mental health, a pattern that is stronger for girls and early life adversity may partially explain this association."
- Nicholas, L., & Tredoux, C. (1996). "Early, late and non-participants in sexual intercourse: A profile of black South African first-year university students". International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling, 19 (2), 111–117
- NewgonWiki: In this study 267 students experienced first sexual intercourse at or before 15 years. 370 students experienced first sexual intercourse at or after 18 years. The authors report this result: "Seventy-six percent of early starters reported greater satisfaction with their first sexual intercourse than did late starters (55%) (i.e., greatly enjoying, or simply enjoying sex).“
- Larsson, I. & Svedin, C. G. (2001). "Sexual experiences in childhood: young adult's recollections," Arch Sex Behav, 31(3):263-73
- In a 2002 study of 269 Swedish students, 30% of those who had a sexual experience with a peer before the age of 13 assessed the activity as having had a positive effect on them as an adult, 66% thought it had no positive or negative effects, and 4% reported a negative effect. Except one, all of the subjects who reported a negative effect were involved in coercive activities.
- Donahue, K. L., Lichtenstein, P., Långström, N., & D’Onofrio, B. M. (2013). Why does early sexual intercourse predict subsequent maladjustment? Exploring potential familial confounds. Health Psychology, 32(2), 180–189.
- "Conclusions: Early intercourse may be associated with poor psychosocial health largely due to shared familial influences rather than through a direct causal connection. Therefore, effective and efficient interventions should address other risk factors common to early intercourse and poor psychosocial health"
- Levine, J. (1996). "A Question of Abuse," Mother Jones.
- "What's wrong with these things? "They make parents nervous," says Allie Kilpatrick, a social work professor at the University of Georgia who conducted a massive review of the literature on childhood sexual experiences, both wanted and unwanted, and administered her own 33-page questionnaire to 501 Southern women. Most of Kilpatrick's subjects had kissed and hugged, fondled and masturbated as adolescents, and more than a quarter had had vaginal intercourse. Her conclusion: "The majority of young people who experience some kind of sexual behavior find it pleasurable, without much guilt, and with no harmful consequences." A similar study of 526 New England undergraduates revealed "no differences...between sibling, nonsibling, and no-[sexual]-experience groups on a variety of adult sexual behavior and sexual adjustment measures."

- Harden, K., Mendle, J., Hill, J., Turkheimer, E., and Emery, R. (2008). "Rethinking timing of first sex and delinquency," Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 37(4), 373-385.
- "The relation between timing of first sex and later delinquency was examined using a genetically informed sample of 534 same-sex twin pairs from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health, who were assessed at three time points over a 7-year interval. [...] After controlling for these genetic and environmental confounds using a quasi-experimental design, earlier age at first sex predicted lower levels of delinquency in early adulthood. [...]
- Although the current results are contrary to embedded assumptions, they are actually consistent with previous research. Specifically, three quasi-experimental (longitudinal or behavior genetic) studies that examined whether timing of first sex influences subsequent psychosocial functioning, controlling for psychological differences that precede sexual initiation, have all failed to find adverse effects for sexual timing. [...]
- The current study suggests that there may be positive functions for early initiation of sexual activity, in that the co-twin with earlier age at first sex demonstrated lower levels of delinquency in early adulthood. This result echoes a small but important body of previous research. In one of the first pieces of sex research, Kinsey et al. (1953) concluded that premarital sexual activity resulted in minimal "psychological disturbance" and may result in healthier non-romantic relationships and greater happiness later in life. More recent research has indicated that early sexual timing is associated with popularity (Prinstein et al. 2003); high self-esteem (for a review see Goodson et al. 2006; Paul et al. 2000); positive self-concept (Pedersen et al. 2003); high levels of body pride (Lammers et al. 2000), and increasing closeness to the same-sex best friend (Billy et al. 1988). [...] In the domain of adult sexual functioning, earlier age at first sex was found to predict greater coital orgasmic capacity in adult women (Raboch and Bartak 1983) and to discriminate sexually functional versus non-functional older men (age 64 years; Vallery-Masson et al. 1981). Women reporting an earlier age at first sex demonstrate less reactivity and faster recovery (as measured by cortical response) in response to stress (Brody 2002)."
- Arreola, Sonya; Neilands, Torsten; Pollack, Lance; Paul, Jay; Catania, Joseph (2008). "Childhood Sexual Experiences and Adult Health Sequelae Among Gay and Bisexual Men: Defining Childhood Sexual Abuse," Journal of Sex Research, 45(3), pp. 246 - 252.
- "Those who had forced sex were significantly more likely to be depressed or have suicidal ideation than those who had consensual sex and those who had no sex before age 18. There was no difference between the consensual sex group and those who had no sex before age 18. The level of well-being was significantly higher for the consensual group compared with the no sex before 18 group and the forced sex group. The latter two groups did not differ from each other on well-being. [...] Interestingly, the forced sex group and the no sex group were statistically indistinguishable in their level of well-being, while the consensual sex group was significantly more likely to have a higher level of well-being than either of the other two groups. This suggests that consensual sex before 18 years of age may have a positive effect, perhaps as an adaptive milestone of adolescent sexual development." This study was inclusive of both minor-minor relations and adult-minor relations; no distinctions were made.
- Meier, A. M. (2007). "Adolescent First Sex and Subsequent Mental Health." American Journal of Sociology, 112(6), 1811–1847.
- Editor note: A more up-to date analysis of this study's findings would surely do a better job of identifying confounds of negative outcomes.
- "While some adolescents experience mental health decrements, the majority of those who had first sex did not. This finding highlights the importance of considering contingencies when investigating the effects of life events on mental health. [...] With respect to policy concerned with adolescent sexual activity, recall that welfare reform legislation’s “abstinence only” initiative suggests that nonmarital sex negatively impacts psychological well-being. This study finds mixed evidence on this assertion. On the one hand, I find support for statistically significant negative mental health effects of first sex for those in the aforementioned subgroups. On the other hand, a substantial majority of those who had sex in this sample did not experience changes in mental health. Among those who did see changes in mental health, on the individual level those changes are moderate in size—one-third to three quarters of an SD on the scales of their respective outcome. While relatively few adolescents who had sex exhibit changes in mental health, and the changes are not huge where they exist, changes of this size in these subgroups could amount to substantial shifts in population-level mental health. [...] For example, if those who had sex prior to time 1 did so in part because they had weaker norms against sex, then perhaps first sex would be less consequential for their mental health. If this is the case, the effects of first sex reported by this study may overestimate the true effects among adolescents."
- Bauserman, Robert, and Davis, Clive (1996). "Perceptions of Early Sexual Experiences and Adult Sexual Adjustment," International Journal of Sexual Health, 8(3), 37-59.
- "Results supported the hypotheses that positively evaluated early sexual experiences would be associated with greater erotophilia, more acceptance of various sexual behaviors for self and others, and greater sexual satisfaction." (From abstract.)
Prevalence and diversity
Most prevalence data is limited to parentally-observed behaviour. Surveys show decreasing rates of sexual intercourse before age 13 in America.[4]

- McKee, Alan (2010). Does pornography harm young people? Australian Journal of Communication, 37(1), pp. 17-36.
- "In a 1996 study 59% of adults surveyed said that they ‘recalled at least one sexual experience with another child during their childhood’ (Haugaard, 1996, p. 86). A 1993 retrospective study of 128 women found that 85% described ‘a childhood sexual game experience’ (Lamb and Coakley, 1993, p. 515)."
- "And in a 2002 study in Sweden 64% of girls aged 3-6 looked at other children’s genitals occasionally, sometime or often; 20% showed their genitals to children; 8% tried to look at nude pictures; 48% played doctors; 18% masturbated; 21% tried to touch other children’s genitals; and 43% touched their genitals at home (Larsson and Svedin, 2002, p.255). Meanwhile, in the same study, 65% of 3-6 year old boys looked at other children’s genitals; 50% tried to look at people undressing; 34% showed their genitals to other children; 8% tried to look at nude pictures; 37% played doctors; 28% masturbated; and 71% touched their genitals at home (Larsson and Svedin, 2002, p. 256)."
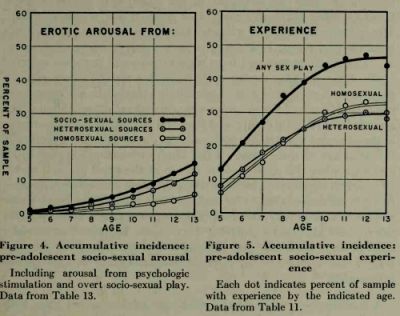
- Veraa, A. (2009). Child Sexual Abuse: The Sources of Anxiety Making and the Negative Effects. IPT Journal, vol 18.
- "Much research since then has strongly supported the notion that children are sexual beings. It has been shown that children, without prompting by adults, think sexually, may engage in a wide range of sexual activities, and enjoy them despite sanctions imposed by adults. (Langfelt, 1981; Martinson, 1981; Goldman and Goldman, 1982[7]; 1988; Haugaard and Tilly, 1988; Okami, 1992; Paris, 1997; Sandfort, 2001; Bancroft, 2003; Denov, 2003). It has also been long known that adult/child sexual activities in other cultures, such as routine stimulation of infant’s and children’s genitals and actively instructing them as to the pleasure of sex, has produced positive rather than negative effects on children. (Ford and Beach, 1951; Yates, 1978; Herlihy, 1993; Barr, 1996; Paris, 1997). Also see Kincaid, (1998). The distaste of child sexuality in our culture seems therefore induced and not intrinsic; culturally or religiously relative, in other words."
- Martinson, Floyd M. (1973). Infant and Child Sexuality: A Sociological Perspective. The Book Mark.
- "By twelve years of age, approximately one boy in every four or five has tried at least to copulate with a female and more than ten percent of preadolescent boys experience their first ejaculation in connection with heterosexual intercourse, according to Kinsey. Ramsey reported that about one-third of his sample of middle-class boys had attempted sexual intercourse."
- Ford. C. S.. & Beach. F. A. (1951). Patterns of sexual behavior. New York: Harper & Row.
- "As long as the adult members of a society permit them to do so, immature males and females engage in practically every type of sexual behavior found in grown men and women. [p. 197] [...] After reviewing the cross-species and cross-cultural evidence, we are convinced that tendencies toward sexual behavior before maturity and even before puberty are genetically determined in many primates, including human beings."
- Reynolds, M.A., Herbenick, D. L., & Bancroft, J. (2003). The nature of childhood sexual experiences: Two studies 50 years apart. In J. Bancroft (Ed.), Sexual Development in Childhood (pp. 134-155). Indiana: Indiana University Press.
- Editor: In a 1999 study of undergraduate students, 5.2% of females and 12.8% of males reported having engaged in sex play with their peers involving genital contact before elementary school, and that 1.3% of girls and 4.0% of boys had engaged in sex play involving anal/genital insertion (with objects or fingers) or oral-genital intercourse before elementary school. By the end of elementary school, the numbers increased to 29.2% for females and 32.9% for males for genital contact and 12.3 for girls and 10.1% for boys for insertion or oral sex. Very little pressure and almost no coercion were reported.
- Thigpen, Jeffry W. (2009). "Early Sexual Behavior in a Sample of Low-Income, African American Children," Journal of Sex Research, 46(1), pp. 67-79.
- "Some recent studies of primarily White, middle-class children have expanded our knowledge of the types of sexual behavior observed in children without known or suspected histories of sexual abuse. These studies show that children engage in sexual play (Lamb & Coakley, 1993; Leitenberg, Greenwald, & Tarran, 1989; Okami, Olmstead, & Abramson, 1997); show interest in viewing the bodies of others, as well as displaying their own (Friedrich, Fisher, Broughton, Houston, & Shafran, 1998; Friedrich, Grambsch, Broughton, Kuiper, & Beilke, 1991; Phipps-Yonas, Yonas, Turner, & Kauper, 1992; Shafran, 1995); and have knowledge of sexual anatomy and function (Gordon, Schroeder, & Abrams, 1990a,b; Grocke, Smith, & Graham, 1995). Taken with the findings from earlier descriptive studies that document the occurrence of such sexual behavior as penile erections in male infants, genital manipulation and play, and masturbation (Kinsey, Pomeroy, & Martin, 1948; Kinsey, Pomeroy, Martin, & Gebhard, 1953; Moll, 1913; Spitz, 1949), non-abused children are suggested to display a wide range of sexual behavior. Behavioral differentiation by gender has been suggested, as genital manipulation and masturbatory behavior have been reported to be more common among boys (Friedrich et al., 1998; Gagnon, 1985; Rutter, 1971). Older children are suggested to be more knowledgeable than younger children about sexual behavior, pregnancy, and sexual abuse prevention (Gordon et al., 1990a), whereas hugging and kissing, self-stimulation, and exhibitionism are reported to be more common among younger children (Friedrich et al., 1991; Kinsey et al., 1948). The findings of some studies have noted an inverse relation between age and childhood sexual behavior, suggesting that the sexual behavior of children becomes covert over time (Friedrich et al., 1998; Friedrich et al., 1991; Gagnon, 1985)."
- Yates, A. (2004). "Biologic perspective on early erotic development," Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 13(3), 479-496.
- "Eighty-five percent of young university women recalled erotic games and 44% recalled erotic games that involved boys [79]. Most remembered feeling sexually aroused or excited at the time. Most of the play involved exposing or touching the genitals. Insertion of objects in the vagina and oral contact was distinctly unusual. Other studies confirmed that most young adult students recalled early sex play that they viewed in a positive light as pleasurable and exciting [40, 80 and 81]."
- Clellan S. Ford and Frank A. Beach (1951) Patterns of Sexual Behavior. New York: Harper and Row
- In their examination of 191 cultures, Clellan S. Ford and Frank A. Beach concluded that as “long as the adult members of a society permit them to do so, immature males and females engage in practically every type of sexual behavior found in grown men and women.”
- Bhugra, D. (2000). Disturbances in objects of desire: Cross-cultural issues. Sexual and Relationship Therapy, 15(1), 67–78. doi:10.1080/14681990050001574
- "In their cross-cultural study of the sexual thoughts of children, Goldman and Goldman (1982) found that 50% of boys [Editor: actually 5%, not 50%, check in the original paper, p.188] and 9.5% of girls expressed aversion to their biological sex. This reaction peaked in adolescence, with 30% of 13-year-old boys in Australia and 20% in the USA expressing such feelings which, by contrast, were virtually absent in Sweden. Bancroft (1989) suggests that the more rigid the sex role stereotypes in a society, the greater the likelihood of this gender dysphoria. Thus, rigid expectations could produce anxiety and insecurity about gender identity, for which transsexual ideas would offer one method of coping."
Factors of earlier sexual development
There is an assumption that cultural sexual restrictions are responsible for the timing of sexual development. While this may be true at some point, there are many other powerful factors that influence timing.
- Ellis, B. J., & Essex, M. J. (2007). Family environments, adrenarche and sexual maturation: A longitudinal test of a life history model. Child Development, 78, 1799–1817.
- "Higher quality parental investment (from both mothers and fathers) and less father-reported Marital Conflict/Depression forecast later adrenarche. Older age at menarche in mothers, higher socioeconomic status, greater mother-based Parental Supportiveness, and lower third-grade body mass index each uniquely and significantly predicted later sexual development in daughters. Consistent with a life history perspective, quality of parental investment emerged as a central feature of the proximal family environment in relation to pubertal timing."
- Ellis, B. J., Figueredo, A. J., Brumbach, B. H., & Schlomer, G. L. (2009). The impact of harsh versus unpredictable environments on the evolution and development of life history strategies. Human Nature, 20, 204–268.
- "The theory posits that clusters of correlated LH [life history] traits (e.g., timing of puberty, age at sexual debut and first birth, parental investment strategies) lie on a slow-to-fast continuum; that harshness (externally caused levels of morbidity-mortality) and unpredictability (spatial-temporal variation in harshness) are the most fundamental environmental influences on the evolution and development of LH strategies; and that these influences depend on population densities and related levels of intraspecific competition and resource scarcity, on age schedules of mortality, on the sensitivity of morbidity-mortality to the organism's resource-allocation decisions, and on the extent to which environmental fluctuations affect individuals versus populations over short versus long timescales.
- Del Giudice M. (2014) Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. Handbook of Life Course Health Development. Cham (CH): Springer; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3
- "In a nutshell, dangerous and unpredictable environments tend to favor fast strategies characterized by early reproduction, sexual promiscuity, unstable relationships, impulsivity, risk taking, aggression, and exploitative tendencies, whereas safe and predictable environments tend to entrain slow strategies characterized by late reproduction, stable relationships, high selfcontrol, aversion to risk, and prosociality. Slow strategies are also favored by nutritional scarcity when danger is low (see Del Giudice et al., 2016; Ellis et al., 2009)"
- "Another recent example is the finding that early adrenarche is associated with reduced white matter volume in the frontal lobe of children (Klauser et al., 2015). Again, the standard interpretation is that early DHEA exposure has a disruptive effect on neurodevelopmenal processes; however, it is also possible that different trajectories of brain development — and even associated “symptoms” such as anxiety and aggressive behaviors — may instead reflect alternative strategies on a fast-slow continuum of life history variation. Ellis and colleagues (2012) present an extended analysis of adolescent risk-taking from this perspective, and discuss several implications for the design of interventions."
Early and middle childhood
- For a recent review, see Li, 2020. and perhaps combine with physical data and observations of Adrenarche as the dawn of advanced adult-like sexuality from our article on cognitive ability. Below are some review highlights.
- Li, Gu. (2022). Sexuality Development in Childhood. 10.1007/978-3-030-84273-4_12. In book: Gender and sexuality development: Contemporary theory and research (pp.323-356) Chapter: 12 Publisher: Springer
- new theoretic frame:
- "[R]esearchers should abolish linear stage models, which incorrectly assume that there is emerging sexual abilities (e.g., kissing), which gradually evolve into full-blown sexual abilities (e.g., having sexual intercourse).[...] sexual activities do not always follow the linear order from kissing to coitus over time"
- solitary activities:
- "Around 40% to 60% of adults recalled having had masturbated in childhood (Bancroft, 2003), and up to 83% of young adults reported having had any type of solitary sexual behavior before adolescence. [...] masturbation in children seldom involves sexual fantasies or sexual attraction as in adults."
- partnered activities ("doctor games"):
- "Past research has suggested that a move as “trivial” as a touch on the hand can illicit physiological and emotional arousal in children that is similar to adults’ sexual experience.[..]These findings suggest that unlike adults, whose erotic feelings are centered around genitalia, children’s erotic feelings are not limited to this area. [...] [I]t is important to recognize that childhood sexual experience is overall positive for most people (Lamb, 2004; Lamb & Coakley, 1993; Larsson & Svedin, 2002a), and that when properly supervised, childhood sexual games could provide a safe context for children to gain sexual knowledge and could have a long-term positive impact on children’s sexuality development"
- sexual arousability is independent from sexual attraction:
- "[C]hildren’s sexual behavior typically does not accompany sexual desire. [...] Surveying 119 boys and 116 girls aged 8 to 11 years, Cameron and Biber (1973) found that 4% of children reported that sex “had been the focus of their thought in the past 5 min [...] 3.9% of men and 2.8% of women recalled thinking a lot about sex between ages 6 to 10 years(Larsson & Svedin, 2002a) [...] young children can be aroused by physical stimulations but without the motivation to seek out sexual encounters and/or the capacity to experience sexual fantasies or sexual attraction. The cause of this dissociation has been attributed to two independent systems governing human sexuality: sexual arousability (i.e., the capacity to become sexually aroused) and sexual proceptivity (i.e., the motivation to have sex)[...] [C]hildren can experience sexual arousal even though they have low levels of endogenous androgens and estrogens"
- onset of sexual attraction:
- "LGB individuals on average have first same-sex sexual attraction at age 10 and heterosexual individuals on average experience first other-sex sexual attraction at the same time"
- sexual orientation fluidity in childhood and early adolescence:
- "[O]ver half of lesbian women and over one third of gay men reported that their first sexual attraction was towards the other sex rather than the same sex [...] Moreover, some self-identified completely heterosexual women and men may experience same-sex sexual attraction or sexual behavior in early adolescence but not in emerging adulthood"
- adrenarche as a hormonal basis for prepubertal sexuality awakening:
- "Adrenarche refers to the “awakening of adrenal gland,” which on average occurs in middle childhood (around 6- to 8-years-old) and is marked by the upsurge of adrenal androgens such as dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) [...] DHEA and its metabolite testosterone improve sexual desire and sexual arousal [...] The link between adrenarche and sexual proceptivity appears to hold universally: A cross-cultural study in New Guinea and the U.S. found that sexual attraction and other proceptive sexual experiences emerge around age 10 years in different cultures, shortly after the onset of adrenache"
- safety or deprivation of intimate peer relationship:
- "the general consensus among researchers is that the dynamics and atmosphere of sexual encounters (e.g., whether these encounters are mutually initiated; whether sexual coercion is involved; whether these encounters take place in a close relationship) have a larger impact on children’s future outcomes than the type of sexual activities (e.g., involving genital contact or not; Diamond et al., 2015; Lamb & Plocha, 2014). [...] Cross-species evidence further suggests that social deprivation of peer interactions in early life may result in persisting deficits in sexual behavior.[...] These findings raise the possibility that peer interactions in childhood, either with the same sex or the other sex, may be essential for the development of later sexual behaviors. However, this hypothesis has not been tested in humans"
- sexual education:
- "starting the discussions before children are in school, creating opportunities to talk, and taking a step-by-step strategy are associated with better communication quality (Gordon et al., 1990; Pluhar et al., 2006; Wilson et al., 2010).[...] In contrast, when parents adopt untrusting, intimidating, or antagonistic approaches or focus on persuading children into sexual abstinence, their children are more likely to hide information from parents"
- promotion of sexual agency:
- "It is widely yet incorrectly assumed that because children have immature self-regulatory systems, they do not exercise sexual reasoning or decision-making (reviewed in Jarkovská & Lamb, 2018). Yet, studies on sexualizing media and sexual scripts have suggested that children do regulate their own sexual behaviors, with their self-regulations being heavily influenced by sexual scripts (APA Task Force on the Sexualization of Girls, 2007). [...] Therefore, one fruitful future direction could be to develop educational, social, and psychological interventions to reduce sexual scripts that prescribe fixed gender and sexual norms and to encourage sexual agency in children."
- new theoretic frame:
- World Health Organization (2010) - Standards for Sexuality Education in Europe
- "Children have sexual feelings even in early infancy. Between the second and third year of their lives, they discover the physical differences between men and women.
- [...]
- During this time, children start to discover their own bodies (early childhood masturbation, self-stimulation) and they may also try to examine the bodies of their friends (playing doctor) […] from the age of three, they understand that adults are secretive about this subject. They test adults’ limits, for instance by undressing without warning or by using sexually charged language."
- Josephs, Lawrence (2015). "How Children Learn About Sex: A Cross-Species and Cross- Cultural Analysis," Archives of Sexual Behavior, 44:1059-1069, DOI: 10.1007/s10508-015-0498-0
- "Nevertheless, the existing but widely scattered primatological and anthropological data indicate that nonhuman primates, hunter-gatherer children, and children in various small tribal cultures from around the world learn about sex through observational learning and sexual rehearsal play prior to puberty. Psychological research in contemporary western contexts indicates that during early childhood children are sexually curious and appear to enjoy pleasure in genital stimulation but contemporary western parents tend to conceal parental sexuality, prohibit interactive sex play, and take a minimalist approach to early childhood sex education in the attempt to preserve childhood sexual innocence."
- Loretta Haroian, Ph.D. (2000, reprint). "Child Sexual Development," Electronic Journal of Human Sexuality, Volume 3, Feb. 1, 2000
- "Two year olds “love to be in the bathroom with other family members. They still like to be naked; they love to romp, flee and pursue, to taste, touch and rub.” [...] “In the later half of the third year, the child begins to feel great tension and expresses it through many compulsive patterns, such as thumb sucking, nose picking, masturbation [...] “Three-and-a-half shifts rapidly between extreme shyness and exhibitionism, all in the quest of positive attention [...] The intense need for attention, preoccupation with bodily functions, interest and curiosity about reproduction and increased ability to communicate verbally with adults can culminate in a pseudo-mature seductive posture, especially in female threes [...] It is quite common at a party of adults to see the 3-year-old daughter of the host comfortably curled up in the lap or laps of a succession of male guests capturing their attention with her interpersonal magnetism. “She may even request that her ‘new friend’ put her to bed and may hold thoughts of him and make reference to him for days or weeks after the party. This behavioral pattern is not exclusive to girls, but is somewhat more pronounced, is better tolerated in terms of gender role stereotypes and receives positive reinforcement from the involved adults [...] “The potential for sexual stimulation in this situation is obvious, and available data confirms the incidence of pedophilic genital fondling at this age [...] The sex histories of many adult men and women contain such experiences that were not traumatic or that caused little concern until the sexual activity escalated beyond looking and fondling or until the situation was discovered and responded to negatively by other adults. [...] Girls at this age are often in love with a considerably older boy or adult male [...] Most children feel that same-sex experimentation is normal and age appropriate, but that heterosexual coupling should be reserved for adulthood and reproduction.”
- Volbert, R. (1997). Sexuelles Verhalten von Kindern: Normale Entwicklung oder Indikator für sexuellen Mißbrauch?[8] In G. Amann & R. Wipplinger (Hrsg.), Sexueller Mißbrauch (S. 385-398). Tübingen: dgvt-Verlag
- [translation] “(…I)n a survey of 211 nursery nurses and kindergarten teachers of the former GDR (Bach, 1993), they stated that they had observed genital games in 75% of boys and 60% of girls aged 2 to 6 years. In a study by Klein (1993), the Erzieherinnen surveyed said that 40% of girls and 19% of boys often played on their genitals. 27% of the Erzieherinnen stated that they had noticed clear states of arousal in the children; orgasms were observed in 13% of the boys and in 17% of the girls. In a Norwegian study (Gundersen et al., 1981), 85% of the Erzieherinnen surveyed stated that they had observed masturbation in the kindergarten children. About a quarter said that it comes to orgasm in the children. In accordance with this, 81% of 91 Erzieherinnen surveyed in a study by Volbert and Zellmer (in prev.), having observed genital games in the children under their care up to 7 years of age; 43% confirmed the observation of masturbation of children and 23% reported having observed that children masturbated to orgasm".
- Del Giudice M. (2014) Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. Handbook of Life Course Health Development. Cham (CH): Springer; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3
- " It is no coincidence that the first sexual and romantic attractions typically develop in middle childhood, in tandem with the intensification of sexual play (Bancroft, 2003; Herdt & McClintock, 2000). By interacting with peers and adults, juveniles receive feedback about the effectiveness of their nascent behavioral strategies."
- "Fetishistic attractions also tend to form in middle childhood, with the onset of pleasurable sensations toward the object of the fetish (e.g., rubber, shoes) that later become fully eroticized (Lawrence, 2009). The onset of fetishistic attractions is part of a generalized awakening of sexuality in middle childhood (Table 1) and illustrates the potential for rapid plasticity with long-lasting outcomes."
- "While learning and play are relatively risk-free, they are not without consequences. The social position achieved in middle childhood is a springboard for adolescence and adulthood; popularity and centrality within the peer network put a child at a considerable advantage, with potentially long-term effects on mating and reproductive success (Del Giudice et al., 2009)."
- Gilbert Herdt and Martha McClintock, Ph.D, The Magical Age of 10, Archives of Sexual Behavior, Vol. 29, No. 6, 2000.
- "Middle childhood should no longer be viewed as a period of hormonal quiescence. Nor should we believe that for all children, there is an absence of sexual subjectivity before gonadarche. Rather, the accumulating evidence suggests that there is more sexual subjectivity occurring during childhood than previously believed, especially from the age of 6 onward, with the onset of adrenarche."
- "It is tempting to argue that if attraction typically develops during adrenarche but is ignored or repressed by adults’ retrospection about sexual development, particularly before it becomes stabilized around the age of 10, the contemporary United States may be a good example of a society in which discontinuity in sexuality is a common developmental experience, and may affect the memory of earliest sexual attraction (Herdt, 1990). Because male and female, as well as homosexual and heterosexual experiences of attraction were found before the age of 10, the internal representation of sexual attraction is robust and memorable enough to overcome these societal constraints (McClintock and Herdt, 1996)."
Fetal/infant sexual capacity
Freud's theories are widely known for their references to autoerotic behaviors in infants.[9][10] Numerous studies have since revealed suspected epilectic seizures in infants to be masturbatory episodes.[11][12][13][14] Further investigations have gone into greater detail, including in-utero obervations:
- Giorgi, Giorgio, and Siccardi, Marco (1996). "Ultrasonographic observation of a female fetus' sexual behavior in utero," American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 175, 3(1, part 1), 753.
- "We recently observed a female fetus at 32 weeks' gestation touching the vulva with the fingers of the right hand. The caressing movements were centered primarily on the region of the clitoris. Movements stopped after 30 to 40 seconds and started again after a few minutes. Furthermore, these slight touches were repeated and were associated with short, rapid movements of pelvis and legs. After another break, in addition to this behavior, the fetus contracted the muscles of the trunk and limbs, and then clonicotonic movements of the whole body followed. Finally, she relaxed and rested.
- We observed this behavior for about 20 minutes. The mother was an active and interested witness, conversing with observers about her child's experience.
- Evidence of male fetuses' excitement reflex in utero, such as erection or ″masturbation” movements, has been previously reported.
- The current observation seems to show not only that the excitement reflex can be evoked in female fetuses at the third trimester of gestation but also that the orgasmic reflex can be elicited during intrauterine life. This would agree with the physiologic features of female sexuality: The female sexual response is separate from reproductive functions and doesn't need a full sexual maturity to be explicit."
- Thomson Salo, F. & Paul, C. (2011) Reconsidering parental sexuality, and infant sensual excitement and greed: what is lost in infant mental health without these concepts? World Association for Infant Mental Health.
- "If infants enjoy breastfeeding and enjoy their body generally, this would be a good basis for their sense of identity, self esteem and enjoyable sexuality. The British psychoanalyst, Rosine Perelberg (2007), wrote that, “The ‘right’ amount of erotism is crucial, so that it is not too much, overexciting the child, or too little, without an erotic investment for the baby, which is also so crucial for its relationship with its own body.” [...] One father asked the Maternal and Child Health Nurse if his 4-month-old son could be jealous of the parents “being intimate” – when the baby was lying on the bed beside his parents he cried loudly whenever his father touched his wife’s breasts (McWilliams, pers. comm.14.8.07). Male observers have reported 15-week-old girl babies acting flirtatiously with them. And while gender often seems relatively ignored in Infant Mental Health in the first year, yet by 6 months there is often a difference in the quality of the sensual excitement with which babies respond to adults."
- Yates, A. (2004). "Biologic perspective on early erotic development," Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 13(3), 479-496.
- "William Masters was an obstetrician before he became a sex researcher. He devised a game that he played while waiting for an infant to be born. He would bet that, if it were a boy, he could deliver the infant before the child could produce an erection. He won the game only half of the time."
- Yates, A. (1978). Sex without shame: Encouraging the child's healthy sexual development. New York: William Morrow.
- "He also noted that all girl babies lubricated vaginally in the first four to six hours of life. Infants were born ready and fully equipped. During sleep, spontaneous erections or vaginal lubrications occur every eighty to, ninety minutes throughout the entire life span. (Masters, 1975) Throughout life, sleeping sexual function remains far more reliable. While awake, our conscious anxieties take their toll.
- Masturbation culminating in climax may occur as early as the first month of life. The baby girl is the most enthusiastic and proficient. With unmistakable intent, she crosses her thighs rigidly. With a glassy stare she grunts, rubs, and flushes for a few seconds or minutes. If interrupted, she screams with annoyance. Movements cease abruptly and are followed by relaxation and deep sleep. This sequence occurs many times during the day, but only occasionally at night. The baby boy proceeds with distinct penis throbs and thrusts accompanied by convulsive contractions of the torso. After climax his erection (without ejaculation) quickly subsides and he appears calm and peaceful. Kinsey reports that one boy of eleven months had ten climaxes in an hour and that another of the same age had fourteen in thirty-eight minutes."
- Martinson, Floyd M. (1973). Infant and Child Sexuality: A Sociological Perspective. The Book Mark.
- "Before specifically discussing the affectional and sexual behavior of infants, we will more systematically and conclusively establish that infants have the somato-sensory capacity for erotic behavior. Boy babies are sometimes born with erections, and there is no reason to believe that the capacity for such marked physiological response develops any later in girls. In a study of nine male babies of ages three to twenty weeks, tumescence (penile erection) was observed at least once daily in seven of the nine. (Halverson, 1940). [...] Kinsey (1953, p. 142) reports one record of a seven-month-old infant and records of five infants under one year who were observed to masturbate. Twenty-three girls, three years or younger, appeared to reach orgasm in self stimulation. Kinsey's unpublished interview data contains notations from interviews with a small sample of two year olds and their mothers. One mother reported that her son had the habit of rubbing against a doll's head to masturbate. Another reported that her son's masturbating was deliberate, prolonged, and accompanied by an erection."
- Later article: Eroticism in Infancy and Childhood.
- Martinson, Floyd M. (1981). “The Sex Education of Young Children”, in Sex Education in the Eighties The Challenge of Healthy Sexual Evolution, ed. by Lorna Brown (Plenum Press: New York), pp. 51-82.
- “What sexual capacity, anatomical, physiological, or psychological, does the child possess that could result in sexual interest, behavior, and learning during the earliest years of life? Sexual capacities and their rehearsal are apparent in the infant long before the development of self-consciousness or erotic awakening. Knowledge of such capacity has existed for a very long time. For example, Pouillet reported research that showed the erectal capacity of infant boys almost 100 years ago, noting that all boys exhibited the faculty for erection if the edge of the foreskin of the penis was tickled with a feather (Pouillet, 1883, p. 99).
- Parents, particularly mothers, are a major source of the knowledge that boy babies commonly have spontaneous erections under a variety of conditions-a full bladder, during bathing, during sleep (Conn & Kanner, 1947, p. 339). In a study of nine male babies aged 3 to 20 weeks, Halverson (1940) reported tumescence (penile erection) at least once daily in seven of the nine. Individual responses varied from 5 to 40 erections per day. Tumescence was often accompanied by restlessness, fretting, crying, stretching, and stiffly flexing the limbs. Following detumescence, behavior was in the nature of playful activity or relaxation. In many societies genital stimulation has been used to subdue and relax infants."
- Danielle Egan and Gail Hawkes, Theorizing the Sexual Child in Modernity (Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), p. 79.
- "Every physician conversant with nervous affections and diseases incident to childhood is aware of the fact that manifestations of the sexual instinct may occur in very young children. Baron Richard von Krafft-Ebing (1892/1965) [...] That children were capable of autoerotic activity was never in doubt among nineteenth-century sexologists."
See also
- Floyd Martinson - a pioneer in child sexuality research, contributing more to that field than anyone else in his lifetime
- Floyd M. Martinson, "Infant and Child Sexuality: A Sociological Perspective", The Book Mark, USA, 1973.
- Floyd M. Martinson. (1974) The Quality of Adolescent Sexual Experiences. The Book Mark
- Martinson, Floyd M. (1981). “The Sex Education of Young Children”, in Sex Education in the Eighties The Challenge of Healthy Sexual Evolution, ed. by Lorna Brown (Plenum Press: New York), pp. 51-82.
- Floyd M. Martinson. "The Sexual Life of Children", Bergin & Garvey, 1994
- John Bancroft - a sexologist, former director in Kinsey's Institute who made great contribution into child and adolescence sexuality
- John Bancroft, June Machover Reinisch (1990) Adolescence and Puberty. Oxford University Press
- John Bancroft (2003) Sexual Development in Childhood (Kinsey Institute Series) Indiana University Press
Excerpt Graphic Library
The EGL on Youth Sexuality contains some useful information on this topic. Please feel free to right click, save and upload to your favored character-limited social media service.
-
Declining rates of sexual activity among youth (YRBS)
-
Various research on Teen Pregnancy correlational nonsense
-
Sexual Repression - effects on the young
-
Sexual Behavior in youth and its effects
-
Reading on child sexuality
-
Some reading on the effects of intimacy
-
Jane Rule on treatment of youth
-
NCAC: Justification for protecting children from porn has always been moral
Sociocultural arguments are also somewhat related:
-
Philip Jenkins on "objective" scientific terminology throughout time
-
Gilbert Herdt on the glib reductionism of "pedophile" taxon
-
Chenier - how the "pedophile" concept services mainstream society
-
Ning de Coninck-Smith[15] on the functions of pedophile-hating
-
Gayle Rubin, in Thinking Sex
-
Foucault, 1978, philosophical take on consent
-
A Percy Foundation reviewer on Chloë Taylor, and the concept of an "Ideal Victim" who is permitted to speak
-
What Foucault had to say about identity
-
Thorstad on the modern gay movement and undesirability of assimilationism[16]
-
Thorstad (same article) on similar trends in the modern gay movement
-
De Orio on pressures facing the LGBT Movement
-
De Orio on Queer Identities that don't fit the model of consent
-
De Orio with some observations about the role of Liberals in Sex Offender Panic
-
David M. Halperin warns against "Queer" essentialism in "Saint Foucault: Towards a Gay Hagiography"
-
Harris Mirkin on "consenting adults only" trope among other sexual minorities
-
David Evans on the fragile modern construct of childhood innocence and contrary examples
-
David Evans - further details the cultural underpinnings of childhood innocence
-
David Evans - more on the underpinnings of childhood innocence
-
James Kincaid: Erotic Innocence
-
Egan and Hawkes - Agency
-
Sex Offender Law Exceptionalism, and a possible reason for it
-
Kinsey is quoted on Sex Offender Exceptionalism in this meme, plus his philosophy on child trauma
-
Rene Guyon (1951) on the curious exceptionalism of sex laws
External links
- Sexual Development & Children with Sex Behavior Problems (Part 1 of 3) - First in a series (2, 3) of videos hitting back at the medical culture of problematizing young people's sexuality.
References
- ↑ Kim, H. S. (2015). Sexual Debut and Mental Health Among South Korean Adolescents. The Journal of Sex Research, 53(3), 313–320.
- ↑ Leander, EM.B. Children’s Sexuality and Nudity in Discourse and Images in a Danish Education and Care Journal over 50 Years (1970–2019): The Emergence of “The Child Perpetrator of Sexual Abuse” in an International Perspective. Arch Sex Behav (2022).
- ↑ Exclaim! A Declaration by IPPF, opens with: "Young people are sexual beings. They have sexual needs, desires, fantasies and dreams. It is important for all young people around the world to be able to explore, experience and express their sexualities in healthy, positive, pleasurable and safe ways. This can only happen when young people’s sexual rights are guaranteed." Later on, it is stated that "Young people’s sexual rights are different and more complex than adults’ sexual rights. One reason for this is the widespread denial of young people’s sexuality. There is a common misconception that young people are not, or should not be sexual beings with the exception of certain groups, such as married young people or young people above a certain age. Sexuality is a central aspect of being human during all phases of each person’s life. Another reason why young people’s sexual rights are particularly complex is because of the need to both protect and empower young people. There is a common assumption that young people are incapable of making decisions for themselves, so parents or other adults should have full authority over decisions related to their sexuality. Resistance to recognize young people’s sexuality and their decision- making abilities makes the realization of young people’s sexual rights all the more challenging. One of the most fundamental challenges of working from a rights-based perspective is finding the balance between young people’s right to be protected and their right to participate and take responsibility for exercising their own rights. Since each young person develops at their own pace, there is no universal age at which certain sexual rights and protections gain or lose importance. Therefore, striking the balance between protection and autonomy should be based on the evolving capacities of each individual young person."
- ↑ YRBS
- ↑ Early Sexual Growth and Activity, in: Sexual Behavior in the Human Male (1948) Alfred Kinsey - notable statistics on pre-adolescent and adolescent male sexual behaviours (first orgasm, homosexual and heterosexual activities, etc.)
- ↑ Pre-adolescent sexual development, in: Sexual Behavior in the Human Female (1953) Alfred Kinsey - statistics on pre-adolescent female sexual behaviours (first orgasm, arousal, significance of sex play, etc.)
- ↑ Goldman and Goldman's 1982 study
- ↑ Volbert, identified in Tabu Zone
- ↑ Auto-eroticism
- ↑ "That children were capable of autoerotic activity was never in doubt among nineteenth-century sexologists." See, Danielle Egan and Gail Hawkes, Theorizing the Sexual Child in Modernity (Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), p. 79.
- ↑ Wulff, C. H., Østergaard, J. R., & Storm, K. (1992). Epileptic fits or infantile masturbation? Seizure, 1(3), 199–201. doi:10.1016/1059-1311(92)90026-w
- ↑ Deda, G., Çaksen, H., Suskan, E., & Gümüs, D. (2001). Masturbation mimicking seizure in an infant. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics, 68(8), 779–781. doi:10.1007/bf02752422
- ↑ Childhood masturbation: Diagnosis of pseudoepileptic seizures in children
- ↑ Doust ZK, Shariat M, Zabandan N, Tabrizi A, Tehrani F. Diagnostic Value of the Urine Mucus Test in Childhood Masturbation among Children below 12 Years of Age: A Cross-Sectional Study from Iran. Iran J Med Sci. 2016 Jul;41(4):283-7. PMID: 27365549; PMCID: PMC4912646.
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Children and Childhood in History and Society
- ↑ Man/boy love and the American gay movement and full text, and our copy









![Ning de Coninck-Smith[15] on the functions of pedophile-hating](/wiki/images/thumb/FLCYK57XwAI5rBj.png/120px-FLCYK57XwAI5rBj.png)




![Thorstad on the modern gay movement and undesirability of assimilationism[16]](/wiki/images/thumb/20210920_033904.jpg/120px-20210920_033904.jpg)











