One of our staff members is contributing considerably to a News Archiving service at Mu. Any well educated (Masters, PhD or above) users who wish to make comments on news sites, please contact Jim Burton directly rather than using this list, and we can work on maximising view count.
Research: Cognitive ability: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The often-repeated ageist/ableist myth<ref>[https://slate.com/technology/2022/11/brain-development-25-year-old-mature-myth.html Slate: Updated take on the 25y/o brain myth]</ref> of brain development ending at the ages of 18 or 25 started circulating in the late 00s and early 10s,<ref>[https://www.apa.org/monitor/julaug04/brain Brain research advances help elucidate teen behavior]</ref> but the samples were never followed up beyond the age of 25.<ref>[https://www.iflscience.com/does-the-brain-really-mature-at-the-age-of-25-68979 Does The Brain Really Mature At The Age Of 25?]</ref> Historically, similar arguments have been made against Women<ref>[https://sci-hub.se/10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64447-7 Sexual Differentiation of the Human Brain A Historical Perspective]</ref><ref>[https://www.wsj.com/articles/the-history-of-female-brain-studies-reveal-a-lot-11584895362 The History of Female Brain Studies Reveal a Lot - WSJ]</ref><ref>[https://theconversation.com/the-female-brain-why-damaging-myths-about-women-and-science-keep-coming-back-in-new-forms-129310 The ‘female’ brain: why damaging myths about women and science keep coming back in new forms]</ref> (the gender differences while moderate, probably ''exceed'' any teen-adult variations<ref>[https://sci-hub.se/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.12.001 The Trouble with Sex Differences]</ref><ref>[https://sci-hub.se/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.02.026 Dump the “dimorphism”: Comprehensive synthesis of human brain studies reveals few male-female differences beyond size]</ref>) and Black people.<ref>[https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/handle/2027.42/49594/1000050402_ftp.pdf SOME RACIAL PECULIARITIES OF THE NEGRO BRAIN]</ref><ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10143281/ Goldstein HW, Yusko KP, Scherbaum CA, Larson EC. Reducing Black-White Racial Differences on Intelligence Tests Used in Hiring for Public Safety Jobs. J Intell. 2023 Mar 28;11(4):62. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence11040062. PMID: 37103247; PMCID: PMC10143281.]</ref> Such alleged "racial peculiarities" are ignored by modern-day authoritarians, who prefer to ideologically mobilize "brain science" in a more selective manner. | The often-repeated ageist/ableist myth<ref>[https://slate.com/technology/2022/11/brain-development-25-year-old-mature-myth.html Slate: Updated take on the 25y/o brain myth]</ref> of brain development ending at the ages of 18 or 25 started circulating in the late 00s and early 10s,<ref>[https://www.apa.org/monitor/julaug04/brain Brain research advances help elucidate teen behavior]</ref> but the samples were never followed up beyond the age of 25.<ref>[https://www.iflscience.com/does-the-brain-really-mature-at-the-age-of-25-68979 Does The Brain Really Mature At The Age Of 25?]</ref> Historically, similar arguments have been made against Women<ref>[https://sci-hub.se/10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64447-7 Sexual Differentiation of the Human Brain A Historical Perspective]</ref><ref>[https://www.wsj.com/articles/the-history-of-female-brain-studies-reveal-a-lot-11584895362 The History of Female Brain Studies Reveal a Lot - WSJ]</ref><ref>[https://theconversation.com/the-female-brain-why-damaging-myths-about-women-and-science-keep-coming-back-in-new-forms-129310 The ‘female’ brain: why damaging myths about women and science keep coming back in new forms]</ref> (the gender differences while moderate, probably ''exceed'' any teen-adult variations<ref>[https://sci-hub.se/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.12.001 The Trouble with Sex Differences]</ref><ref>[https://sci-hub.se/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.02.026 Dump the “dimorphism”: Comprehensive synthesis of human brain studies reveals few male-female differences beyond size]</ref>) and Black people.<ref>[https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/handle/2027.42/49594/1000050402_ftp.pdf SOME RACIAL PECULIARITIES OF THE NEGRO BRAIN]</ref><ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10143281/ Goldstein HW, Yusko KP, Scherbaum CA, Larson EC. Reducing Black-White Racial Differences on Intelligence Tests Used in Hiring for Public Safety Jobs. J Intell. 2023 Mar 28;11(4):62. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence11040062. PMID: 37103247; PMCID: PMC10143281.]</ref> Such alleged "racial peculiarities" are ignored by modern-day authoritarians, who prefer to ideologically mobilize "brain science" in a more selective manner. | ||
Further brain imaging investigations have put "adulthood" (when so defined) at least as late as the 30s,<ref>[https://www.bbc.com/news/newsbeat-47622059 BBC - People don't become 'adults' until their 30s, say scientists]</ref> | Further brain imaging investigations have put "adulthood" (when so defined) at least as late as the 30s, with one study bizarrely concluding that the brain stays in the same "phase" between 9 and the early 30s.<ref>[https://www.bbc.com/news/newsbeat-47622059 BBC - People don't become 'adults' until their 30s, say scientists], [https://www.aol.com/articles/adolescence-lasts-30s-study-shows-101116917.html Adolescence lasts until 30s]</ref> Ultimately, no set age for the end of brain "development" and beginning of "deterioration" has ever been established, as this is an impossible task and riddled with subjective factors. ''Neuroplasticity'' (and adaptive interpretation thereof) is a massive pitfall here, and in teenagers, it is generally over-claimed. Plasticity is also a troublesome argument for [[Ageism|ageists]] to maintain, as they also hold that critical thinking (known to promote plasticity) is considerably degraded in teens. | ||
In summary, it can be said that the perceived incompetence of the modern minor is exaggerated and culture-bound, owing somewhat to the highly lucrative "[[Adolescence|troubled teen]]" industry and the advocacy science surrounding it. | In summary, it can be said that the perceived incompetence of the modern minor is exaggerated and culture-bound, owing somewhat to the highly lucrative "[[Adolescence|troubled teen]]" industry and the advocacy science surrounding it. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Well known data surrounding the high recidivism and reoffending rates of youth offenders also contradicts the "unique plasticity" or [[Research: Who offends and how often?|"second chance" narrative]] (sources in linked article). So like many MAP-adjacent topics, the source of the myth is a classical case of "bad science following good (or at least political) intentions". Since this Supreme Court decision, some less reputable brain scientists have cottoned on to the trend, sometimes making spurious claims that contradict their own experimental findings - one supposes, in an attempt to curry favor. The MacArthur Foundation, who manage a $7.0bn endowment, are one example of a private foundation who plowed considerable finance into a now-discontinued program - adding to the now increasingly outdated and discredited "teen brain" body of research.<ref>[https://www.macfound.org/networks/research-network-on-adolescent-development-juvenil MacArthur Foundation: Research Network on Adolescent Development]</ref> | Well known data surrounding the high recidivism and reoffending rates of youth offenders also contradicts the "unique plasticity" or [[Research: Who offends and how often?|"second chance" narrative]] (sources in linked article). So like many MAP-adjacent topics, the source of the myth is a classical case of "bad science following good (or at least political) intentions". Since this Supreme Court decision, some less reputable brain scientists have cottoned on to the trend, sometimes making spurious claims that contradict their own experimental findings - one supposes, in an attempt to curry favor. The MacArthur Foundation, who manage a $7.0bn endowment, are one example of a private foundation who plowed considerable finance into a now-discontinued program - adding to the now increasingly outdated and discredited "teen brain" body of research.<ref>[https://www.macfound.org/networks/research-network-on-adolescent-development-juvenil MacArthur Foundation: Research Network on Adolescent Development]</ref> | ||
[[ | Our [[Debate_Guide:_Teen_brain|Teen Brain debate guide]] offers rebuttals to these myths; use it together with the following sources: | ||
==Basic Physiology/volumes== | ==Basic Physiology/brain volumes== | ||
Total brain volume ''and'' Gray Matter volume appears to reach a peak at the start of, or during puberty<ref>Cabana T, Jolicoeur P, and Michaud J (1993) Prenatal and postnatal growth and allometry of stature, head circumference, and brain weight in Quebec children. Am. J. Hum. Biol.5:93–99.</ref><ref>[https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.06.08.447489v3.full.pdf Brain charts for the human lifespan - Bethlehem et al (2022)]</ref>, declining thereafter. White matter, which has a less critical function in cognition, takes until the mid-40s to peak in volume. It is clear that some parts of the brain develop into and beyond early adulthood, while others might regress somewhat. This is a normal process of aging, since brain development and cognitive capacity are highly elastic and dependent upon one's environment. | Total brain volume ''and'' Gray Matter volume appears to reach a peak at the start of, or during puberty<ref>Cabana T, Jolicoeur P, and Michaud J (1993) Prenatal and postnatal growth and allometry of stature, head circumference, and brain weight in Quebec children. Am. J. Hum. Biol.5:93–99.</ref><ref>[https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.06.08.447489v3.full.pdf Brain charts for the human lifespan - Bethlehem et al (2022)]</ref>, declining thereafter. White matter, which has a less critical function in cognition, takes until the mid-40s to peak in volume. It is clear that some parts of the brain develop into and beyond early adulthood, while others might regress somewhat. This is a normal process of aging, since brain development and cognitive capacity are highly elastic and dependent upon one's environment. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*'''Del Giudice, M, (2014). "[https://marcodgdotnet.files.wordpress.com/2014/11/delgiudice_2014_middle-childhood_synthesis_cdp.pdf Middle Childhood: An Evolutionary-Developmental Synthesis]", ''Child Development Perspectives'', Volume 8, Number 4, Pages 193–200.''' | *'''Del Giudice, M, (2014). "[https://marcodgdotnet.files.wordpress.com/2014/11/delgiudice_2014_middle-childhood_synthesis_cdp.pdf Middle Childhood: An Evolutionary-Developmental Synthesis]", ''Child Development Perspectives'', Volume 8, Number 4, Pages 193–200.''' | ||
*:Del Giudice has age 6-8 as the peak for gray matter (see tables). This paper also goes into detail about development in middle-childhood, most importantly the onsent of '''adrenarche'''<ref>Gilbert Herdt and Martha McClintock, Ph.D, [https://www.ipce.info/sites/ipce.info/files/biblio_attachments/herdt_-_the_magical_age_of_10_2000.pdf ''The Magical Age of 10''], in ''Archives of Sexual Behavior'', Vol. 29, No. 6, 2000. </ref> between 6-8 years of age, giving rise to sexual differentiation in behavior - including sexual curiosity and attraction. It could be argued that as a developmental milestone, this age is as important, if not more so than the start of puberty, as determined by thelarche or gonardarche. | *:Del Giudice has age 6-8 as the peak for gray matter (see tables). This paper also goes into detail about development in middle-childhood, most importantly the onsent of '''adrenarche'''<ref>Gilbert Herdt and Martha McClintock, Ph.D, [https://www.ipce.info/sites/ipce.info/files/biblio_attachments/herdt_-_the_magical_age_of_10_2000.pdf ''The Magical Age of 10''], in ''Archives of Sexual Behavior'', Vol. 29, No. 6, 2000. </ref> between 6-8 years of age, giving rise to sexual differentiation in behavior - including sexual curiosity and attraction. It could be argued that as a developmental milestone, this age is as important, if not more so than the start of puberty, as determined by thelarche or gonardarche. | ||
*:"By age 6, the brain has almost reached its maximum size and receives a decreasing share of the body’s glucose after the consumption peak of early childhood (see Figure 1; Giedd & Rapoport, 2010; Kuzawa et al., in press). However, brain development proceeds at a sustained pace, with intensive synaptogenesis in cortical areas (gray matter) and rapid maturation of axonal connections (white matter; Lebel, Walker, Leemans, Phillips, & Beaulieu, 2008). | *:"By age 6, the brain has almost reached its maximum size and receives a decreasing share of the body’s glucose after the consumption peak of early childhood (see Figure 1; Giedd & Rapoport, 2010; Kuzawa et al., in press). However, brain development proceeds at a sustained pace, with intensive synaptogenesis in cortical areas (gray matter) and rapid maturation of axonal connections (white matter; Lebel, Walker, Leemans, Phillips, & Beaulieu, 2008). [...] The most dramatic changes probably occur in the domain of self-regulation and executive functions: Children become much more capable of inhibiting unwanted behavior, maintaining sustained attention, making and following plans, and so forth (Best, Miller, & Jones, 2009; Weisner, 1996)." | ||
*'''Mousley, A., Bethlehem, R. A. I., Yeh, F. C., & Astle, D. E. (2025). [https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12647875/ Topological turning points across the human lifespan.] ''Nature communications'', 16(1), 10055. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-65974-8''' | |||
::"[W]e identified four major topological turning points across the lifespan – around nine, 32, 66, and 83 years old." | |||
::“The second lifespan epoch, ages nine to 32, indicates that the trajectory of topological development remains consistent across this period. While adolescence begins with puberty, the end of adolescence is less clear, with older definitions ending before 20 and more recent definitions extending into the mid-20s. The transition to adulthood is influenced by cultural, historical, and social factors, making it context-dependent rather than a purely biological shift. Our findings suggest that in Western countries (i.e., the United Kingdom and United States of America), adolescent topological development extends to around 32 years old, before brain networks begin a new trajectory of topological development.” | |||
==Competence== | ==Competence== | ||
it's widely believed that minors differ fundamentally in their cognitive and decision-making abilities from adults. In addition legal definitions are often conflated with real capacities of people, leading to belief in a clear boundary between competent and incompetent ages. Many studies refuse this view, supporting the concept of [[Evolving capacity|evolving capacity]]. | it's widely believed that minors differ fundamentally in their cognitive and decision-making abilities from adults. In addition legal definitions are often conflated with real capacities of people, leading to belief in a clear boundary between competent and incompetent ages. Many studies refuse this view, supporting the concept of [[Evolving capacity|evolving capacity]]. | ||
*'''Kidd, C (2025) in ''The Conversation''. [https://theconversation.com/children-can-be-systematic-problem-solvers-at-younger-ages-than-psychologists-had-thought-new-research-266438 Children can be systematic problem-solvers at younger ages than psychologists had thought – new research]''' | |||
*:"More than half the children we tested demonstrated evidence of structured algorithmic thinking, and at ages as young as 4 years old. While older kids were more likely to use algorithmic strategies, our finding contrasts with Piaget’s belief that children were incapable of this kind of systematic strategizing before 7 years of age. Our results suggest that children are actually capable of spontaneous logical strategy discovery much earlier when circumstances require it. Explaining our results requires a more nuanced interpretation of Piaget’s original data. While children may still favor apparently less logical solutions to problems during the first two Piagetian stages, it’s not because they are incapable of doing otherwise if the situation requires it." | |||
*'''Johnson SB, Blum RW, Giedd JN. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2892678/ Adolescent maturity and the brain: the promise and pitfalls of neuroscience research in adolescent health policy.] J Adolesc Health. 2009 Sep;45(3):216-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.05.016.''' | *'''Johnson SB, Blum RW, Giedd JN. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2892678/ Adolescent maturity and the brain: the promise and pitfalls of neuroscience research in adolescent health policy.] J Adolesc Health. 2009 Sep;45(3):216-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.05.016.''' | ||
| Line 44: | Line 52: | ||
*:"one consequence of this framework would be the need to abandon the goal of identifying a single age-of-brain maturity. Rather, there would be a suite of maturity points that reflect different neural systems and different associated behaviors. For example, an individual could reach an age of “baseline cognitive maturity”—the capacity to engage in goal-directed behavior under neutral, non-distracted circumstances, substantially earlier than an age of “cognitive-emotional maturity”—the capacity to maintain goal-directed behavior in the face of competing emotional cues." | *:"one consequence of this framework would be the need to abandon the goal of identifying a single age-of-brain maturity. Rather, there would be a suite of maturity points that reflect different neural systems and different associated behaviors. For example, an individual could reach an age of “baseline cognitive maturity”—the capacity to engage in goal-directed behavior under neutral, non-distracted circumstances, substantially earlier than an age of “cognitive-emotional maturity”—the capacity to maintain goal-directed behavior in the face of competing emotional cues." | ||
*'''Epstein, Robert (2010). "Adultness | *'''Epstein, Robert (2010). chapter "Adultness" in''"Teen 2.0"'', 148-157.''' | ||
*:"After reviewing the relevant scientific literature, interviewing many adults, and consulting with three other psychologists and two psychiatrists with expertise in adult development issues, we concluded that there are fourteen different skill-sets or "competencies" [love, sex, leadership, problem solving, physical abilities, verbal and math, interpersonal skills, responsibility, managing high-risk behaviors, work, education, personal care, self-management, and citizenship] that distinguish adults from non-adults. [...] For three of the competencies--love, leadership and problem solving--we did find statistically significant differences between the mean scores of teens and adults, with adults outscoring the teens. But the absolute differences were small. [...] On two other scales--work and self-management--the differences between the adult scores and teen scores were marginally significant (at the .05 level), again in the adults' favor, but the absolute differences were less than 4 percent. On the other nine scales, we found no significant differences at all between the adult and teen scores. [...] fifty five of the adults in our sample were college graduates--more than double the rate of college graduates in the United States." | *:"After reviewing the relevant scientific literature, interviewing many adults, and consulting with three other psychologists and two psychiatrists with expertise in adult development issues, we concluded that there are fourteen different skill-sets or "competencies" [love, sex, leadership, problem solving, physical abilities, verbal and math, interpersonal skills, responsibility, managing high-risk behaviors, work, education, personal care, self-management, and citizenship] that distinguish adults from non-adults. [...] For three of the competencies--love, leadership and problem solving--we did find statistically significant differences between the mean scores of teens and adults, with adults outscoring the teens. But the absolute differences were small. [...] On two other scales--work and self-management--the differences between the adult scores and teen scores were marginally significant (at the .05 level), again in the adults' favor, but the absolute differences were less than 4 percent. On the other nine scales, we found no significant differences at all between the adult and teen scores. [...] fifty five of the adults in our sample were college graduates--more than double the rate of college graduates in the United States." | ||
*'''Epstein, Robert (2007). "[http://drrobertepstein.com/pdf/Epstein-THE_MYTH_OF_THE_TEEN_BRAIN-Scientific_American_Mind-4-07.pdf The Myth of the Teen Brain]," ''Scientific American Mind'', April/May, 57-63.''' | *'''Epstein, Robert (2007). "[http://drrobertepstein.com/pdf/Epstein-THE_MYTH_OF_THE_TEEN_BRAIN-Scientific_American_Mind-4-07.pdf The Myth of the Teen Brain]," ''Scientific American Mind'', April/May, 57-63.''' | ||
*:"Visual acuity, for example, peaks around the time of puberty. "Incidental memory"—the kind of memory that occurs automatically, without any mnemonic effort, peaks at about age 12 and declines through life. [...] In the 1940s pioneering intelligence researchers J. C. Raven and David Wechsler, relying on radically different kinds of intelligence tests, each showed that raw scores on intelligence tests peak between ages 13 and 15 and decline after that throughout life. Although verbal expertise and some forms of judgment can remain strong throughout life, the extraordinary cognitive abilities of teens, and especially their ability to learn new things rapidly, is beyond question. And whereas brain size is not necessarily a good indication of processing ability, it is notable that recent scanning data collected by Eric Courchesne and his colleagues at the University of California, San Diego, show that brain volume peaks at about age 14." | *:"Visual acuity, for example, peaks around the time of puberty. "Incidental memory"—the kind of memory that occurs automatically, without any mnemonic effort, peaks at about age 12 and declines through life. [...] In the 1940s pioneering intelligence researchers J. C. Raven and David Wechsler, relying on radically different kinds of intelligence tests, each showed that raw scores on intelligence tests peak between ages 13 and 15 and decline after that throughout life. Although verbal expertise and some forms of judgment can remain strong throughout life, the extraordinary cognitive abilities of teens, and especially their ability to learn new things rapidly, is beyond question. And whereas brain size is not necessarily a good indication of processing ability, it is notable that recent scanning data collected by Eric Courchesne and his colleagues at the University of California, San Diego, show that brain volume peaks at about age 14." | ||
*:"A variety of research in several fields suggests that teen turmoil is caused by cultural factors, not by a faulty brain. [...] Anthropological research reveals that teens in many cultures experience no turmoil whatsoever and that teen problems begin to appear only after Western schooling, movies and television are introduced. [...] Teens have the potential to perform in exemplary ways, the author says, but we hold them back by infantilizing them and trapping them in the frivolous world of teen culture." | |||
*:"Studies of intelligence, perception and memory show that teens are in many ways superior to adults. [...] When we treat teens like adults, they almost immediately rise to the challenge." | |||
*'''Moshman, David (2011). "[https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9780203835111/adolescent-rationality-development-david-moshman Adolescent Rationality and Development: Cognition, Morality, and Identity, Third Edition].''' | *'''Moshman, David (2011). "[https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9780203835111/adolescent-rationality-development-david-moshman Adolescent Rationality and Development: Cognition, Morality, and Identity, Third Edition].''' | ||
| Line 59: | Line 69: | ||
*:"Perhaps most intriguing are the age-related trajectories for raw score performance. For most tasks, proficiency improved dramatically between 6 and 10 years of age, leveling off during early adolescence (approximately 10 to 12 years of age), suggesting that for many neurocognitive tasks, children approach adult levels of performance at that age. For a few measures, scores increased linearly throughout the age range. These were tasks that assessed basic information processing, such as Coding, Digit Span, and Spatial Span. Still others were associated with a non-linear component during adolescence. Some showed a flattening of the curve followed by another period of acceleration, suggesting another spurt in mid-adolescence. Verbal learning actually reversed direction with performance declining in later adolescence." | *:"Perhaps most intriguing are the age-related trajectories for raw score performance. For most tasks, proficiency improved dramatically between 6 and 10 years of age, leveling off during early adolescence (approximately 10 to 12 years of age), suggesting that for many neurocognitive tasks, children approach adult levels of performance at that age. For a few measures, scores increased linearly throughout the age range. These were tasks that assessed basic information processing, such as Coding, Digit Span, and Spatial Span. Still others were associated with a non-linear component during adolescence. Some showed a flattening of the curve followed by another period of acceleration, suggesting another spurt in mid-adolescence. Verbal learning actually reversed direction with performance declining in later adolescence." | ||
*'''Adler, N.E., & Matthews, K. (1994). "Why do | *'''Adler, N.E., & Matthews, K. (1994). "Health Psychology: Why do Some People Get Sick and Some Stay Well?," ''Annual Review of Psychology'', 45, 229-259.''' | ||
*:"However, empirical tests show that adolescents are no less rational than adults. Applications of rational models to adolescent decision-making show that adolescents are consistent in their reasoning and behavior after the salient set of beliefs is assessed (Adler et al 1990). Quadrel et al (1993) demonstrated that adolescents are no more biased in their estimates of vulnerability to adverse health outcomes than are their parents." | *:"However, empirical tests show that adolescents are no less rational than adults. Applications of rational models to adolescent decision-making show that adolescents are consistent in their reasoning and behavior after the salient set of beliefs is assessed (Adler et al 1990). Quadrel et al (1993) demonstrated that adolescents are no more biased in their estimates of vulnerability to adverse health outcomes than are their parents." | ||
| Line 81: | Line 91: | ||
*'''Del Giudice M. (2014) [https://iris.unito.it/retrieve/handle/2318/1853338/974935/DelGiudice_2018_middle-childhood_chapter_pre.pdf Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.]; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543707/ Handbook of Life Course Health Development]. ''Cham (CH): Springer''; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3''' | *'''Del Giudice M. (2014) [https://iris.unito.it/retrieve/handle/2318/1853338/974935/DelGiudice_2018_middle-childhood_chapter_pre.pdf Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.]; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543707/ Handbook of Life Course Health Development]. ''Cham (CH): Springer''; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3''' | ||
*:"In biological terms, middle childhood corresponds to human juvenility — a stage in which the individual is still sexually immature, but no longer dependent on parents for survival. In social mammals and primates, juvenility is a phase of intense learning — often accomplished through play — in which youngsters practice adult behavioral patterns and acquire essential social and foraging skills." | *:"In biological terms, middle childhood corresponds to human juvenility — a stage in which the individual is still sexually immature, but no longer dependent on parents for survival. In social mammals and primates, juvenility is a phase of intense learning — often accomplished through play — in which youngsters practice adult behavioral patterns and acquire essential social and foraging skills." | ||
*:"The transition to middle childhood is marked by a simultaneous increase in perceptual abilities (including a transition from local to global visual processing), motor control (including the emergence of adult-like walking), and complex reasoning skills (Bjorklund, 2011; Poirel et al., 2011; Weisner, 1996)." | *:"The transition to middle childhood is marked by a simultaneous increase in perceptual abilities (including a transition from local to global visual processing), motor control (including the emergence of adult-like walking), and complex reasoning skills (Bjorklund, 2011; Poirel et al., 2011; Weisner, 1996)." | ||
| Line 87: | Line 96: | ||
*:"On a broader social level, cross-cultural evidence shows that juveniles start “getting noticed” by adults—that is, they begin to be viewed fully as people with their own individuality, personality, and social responsibility (Lancy & Grove, 2011)." | *:"On a broader social level, cross-cultural evidence shows that juveniles start “getting noticed” by adults—that is, they begin to be viewed fully as people with their own individuality, personality, and social responsibility (Lancy & Grove, 2011)." | ||
*:"While children are still receiving sustained investment from parents and other relatives—in the form of food, protection, knowledge, and so forth—they also start to actively contribute to their family economy. By providing resources and sharing the burden of child care, juveniles can boost their parents’ reproductive potential. The dual nature of juveniles as both receivers and providers explains many psychological features of middle childhood and has likely played a major role in the evolution of human life history (Kramer, 2011)." | *:"While children are still receiving sustained investment from parents and other relatives—in the form of food, protection, knowledge, and so forth—they also start to actively contribute to their family economy. By providing resources and sharing the burden of child care, juveniles can boost their parents’ reproductive potential. The dual nature of juveniles as both receivers and providers explains many psychological features of middle childhood and has likely played a major role in the evolution of human life history (Kramer, 2011)." | ||
*'''Lancy, D. F., & Grove, M. A. (2011). [https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1275&context=sswa_facpubs Getting noticed: Middle childhood in cross-cultural perspective.] ''Human Nature'', 22, 281-302.''' | |||
*:"Naming and other rites of passage sometimes acknowledge this transition, but it is, reliably, marked by the assumption or assignment of specific chores or duties.[...] There is also an acknowledgement at the exit from middle childhood, of near–adult levels of competence — as a herdsman or hunter or as gardener or infant-caretaker." | |||
*:"In Jean Piaget’s influential theory of human cognitive development, the period from 5 to 7 years is marked by a major transition from pre-operational to concrete operational thinking (Piaget 1963). From a historical standpoint there is a great deal of evidence that this age range also marked a major transition in children’s social standing, in particular that a 7 year-old could be held legally and morally accountable for his/her actions (White 1991: 13)." | |||
*:"The last point we would make is that the various markers of the onset of middle childhood we have enumerated all seem to be tied to a shift in cognitive functioning. There is an evident sensitivity to the expectations and needs of others—critical in child-minding and errand running. The child displays other indicators of “sense,” including lengthened attention span, greater language facility, and persistence in completing tasks. He or she is a willing student. The manifold signs of awareness of appropriate behavior vis-à-vis sex and gender go along with increased complexity in peer relations and rule-governed play. On the other hand, the exit from middle childhood is signaled more by markers of physical maturity—including secondary sexual characteristics, a growth spurt, voice change, increased sexuality, and augmented strength and endurance." | |||
* '''Wang, F., Tong, Y., & Danovitch, J. (2019). [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333302913_Who_do_I_believe_Children's_epistemic_trust_in_internet_teacher_and_peer_informants Who do I believe? Children’s epistemic trust in internet, teacher, and peer informants]. ''Cognitive Development'', 50, 248–260. Doi:10.1016/j.cogdev.2019.05.006''' | |||
::"Taken together, our findings suggest that school age children can reason about the reliability of information sources from different categories and that their judgments are sensitive to the type of information being sought. Just as children can be skeptical when making judgments about the reliability of different people (see Mills, 2013), children’s belief in information from the internet is not immutable. " | |||
===Informed consent=== | ===Informed consent=== | ||
| Line 97: | Line 114: | ||
=== Child's competence in law === | === Child's competence in law === | ||
* '''Lauren Eade (2001) [https://www5.austlii.edu.au/au/journals/NewcLawRw/2001/16.pdf Legal Incapacity, Autonomy, and Children's Rights], ''Newcastle Law Review 5'', ([https://web.archive.org/web/20130420133701/http://snifferdogonline.com/reports/Child%20Abuse,%20Sexuality%20and%20Violence/Legal%20Incapacity,%20Autonomy,%20and%20Children's%20Rights.pdf a copy])''' | * '''Lauren Eade (2001) [https://www5.austlii.edu.au/au/journals/NewcLawRw/2001/16.pdf Legal Incapacity, Autonomy, and Children's Rights], ''Newcastle Law Review 5'', ([https://web.archive.org/web/20130420133701/http://snifferdogonline.com/reports/Child%20Abuse,%20Sexuality%20and%20Violence/Legal%20Incapacity,%20Autonomy,%20and%20Children's%20Rights.pdf a copy])''' | ||
*:Doli incapax [age of criminal responsibility] and age of consent laws are representative of the two ways in which the law's presumption of children's incapacity denies autonomy even to the actually competent child. One denies autonomy and the fundamental stage of formation of intent; the other refuses to acknowledge the validity of a child's intent in particular areas. Both are devoid of scientific basis. Both are motivated by questionable control motives as well as a desire to protect. And both conceptualise the child in a manner inherently incompatible with the child as rights-holder. | |||
*:But incapacity does not have to be an "all or nothing" issue. There is no reason why incapacity in some areas should deny capacity and autonomy in others, or why a child cannot be protected as well as allowed rights appropriate to his or her level of development. These are only irreconcilable propositions in the current model that presumptively ascribes incapacity to all children. If the law were to abandon its over-protective prejudices and engage with each child individually, judging his or her actual competence, these unjust consequences would be avoided. Immature children could retain the protection of incapacity. Specifically or generally autonomous children could gain recognition of their rights. And the law could at last acknowledge the fundamental fact that each and every child is a distinctly different human being. | |||
==Risk Taking/Impulsivity/Prefrontal Physiology== | ==Risk Taking/Impulsivity/Prefrontal Physiology== | ||
| Line 137: | Line 154: | ||
*'''Del Giudice M. (2014) [https://iris.unito.it/retrieve/handle/2318/1853338/974935/DelGiudice_2018_middle-childhood_chapter_pre.pdf Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.]; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543707/ Handbook of Life Course Health Development]. ''Cham (CH): Springer''; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3''' | *'''Del Giudice M. (2014) [https://iris.unito.it/retrieve/handle/2318/1853338/974935/DelGiudice_2018_middle-childhood_chapter_pre.pdf Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.]; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543707/ Handbook of Life Course Health Development]. ''Cham (CH): Springer''; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3''' | ||
*:"The most dramatic changes probably occur in the domain of self-regulation and executive functions: children become much more capable of inhibiting unwanted behavior, maintaining sustained attention, making and following plans, and so forth (Best, Miller, & Jones, 2009; Weisner, 1996)." | *:"The most dramatic changes probably occur in the domain of self-regulation and executive functions: children become much more capable of inhibiting unwanted behavior, maintaining sustained attention, making and following plans, and so forth (Best, Miller, & Jones, 2009; Weisner, 1996)." | ||
*'''Berns GS, Moore S, Capra CM (2009) Adolescent Engagement in Dangerous Behaviors Is Associated with Increased White Matter Maturity of Frontal Cortex. ''PLoS ONE'' 4(8): e6773. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006773''' | |||
::"The direction of correlation suggests that rather than having immature cortices, adolescents who engage in dangerous activities have frontal white matter tracts that are more adult in form than their more conservative peers." | |||
==Moral reasoning== | ==Moral reasoning== | ||
Latest revision as of 10:02, 25 December 2025
 | ||||||||||||
| Part of NewgonWiki's research project | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| Template: Research - This template |
The often-repeated ageist/ableist myth[1] of brain development ending at the ages of 18 or 25 started circulating in the late 00s and early 10s,[2] but the samples were never followed up beyond the age of 25.[3] Historically, similar arguments have been made against Women[4][5][6] (the gender differences while moderate, probably exceed any teen-adult variations[7][8]) and Black people.[9][10] Such alleged "racial peculiarities" are ignored by modern-day authoritarians, who prefer to ideologically mobilize "brain science" in a more selective manner.
Further brain imaging investigations have put "adulthood" (when so defined) at least as late as the 30s, with one study bizarrely concluding that the brain stays in the same "phase" between 9 and the early 30s.[11] Ultimately, no set age for the end of brain "development" and beginning of "deterioration" has ever been established, as this is an impossible task and riddled with subjective factors. Neuroplasticity (and adaptive interpretation thereof) is a massive pitfall here, and in teenagers, it is generally over-claimed. Plasticity is also a troublesome argument for ageists to maintain, as they also hold that critical thinking (known to promote plasticity) is considerably degraded in teens.
In summary, it can be said that the perceived incompetence of the modern minor is exaggerated and culture-bound, owing somewhat to the highly lucrative "troubled teen" industry and the advocacy science surrounding it.
A little background
This myth began its ascent to folklore after a 2005 US Supreme Court decision preventing teenage offenders from being executed. In their brief, the American Psychological Association successfully,[12] (but fallaciously and contrary to their own earlier Teen Abortion amicus[13]) argued that the teen temperament is uniquely malleable and subject to change. The amicus cites behavioral studies and observations that lack valid comparisons and experimental controls, otherwise identifying trends that are culture-bound or contradicted by other studies cited by Robert Epstein (for example) in this article. Generalizations are wrongly made from physiological data to competences, and then further leaps of faith are made to behaviors and "policy implications".[14][15][16][17] This common fallacy of relevance and the resulting chain of hollow claims (about young people), is typical of advocacy science. One legal scholar even coined the term "Brain Overclaim Syndrome" to describe it.[18]
Well known data surrounding the high recidivism and reoffending rates of youth offenders also contradicts the "unique plasticity" or "second chance" narrative (sources in linked article). So like many MAP-adjacent topics, the source of the myth is a classical case of "bad science following good (or at least political) intentions". Since this Supreme Court decision, some less reputable brain scientists have cottoned on to the trend, sometimes making spurious claims that contradict their own experimental findings - one supposes, in an attempt to curry favor. The MacArthur Foundation, who manage a $7.0bn endowment, are one example of a private foundation who plowed considerable finance into a now-discontinued program - adding to the now increasingly outdated and discredited "teen brain" body of research.[19]
Our Teen Brain debate guide offers rebuttals to these myths; use it together with the following sources:
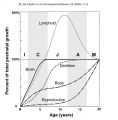
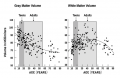
Basic Physiology/brain volumes
Total brain volume and Gray Matter volume appears to reach a peak at the start of, or during puberty[20][21], declining thereafter. White matter, which has a less critical function in cognition, takes until the mid-40s to peak in volume. It is clear that some parts of the brain develop into and beyond early adulthood, while others might regress somewhat. This is a normal process of aging, since brain development and cognitive capacity are highly elastic and dependent upon one's environment.
- Leah H. Somerville. 2016. Searching for Signatures of Brain Maturity: What Are We Searching For? Neuron, 92(6), 1164–1167, doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.059
- "In the neurodevelopmental literature, a given neural measurement is typically interpreted as mature when it matches (to a sufficient degree) an “adult” reference. [...] However, structural development continues to progress for a surprisingly long time. One especially large study showed that for several brain regions, structural growth curves had not plateaued even by the age of 30, the oldest age in their sample (Tamnes et al., 2010; see Figure 1B). [...] Other work focused on structural brain measures through adulthood show progressive volumetric changes from ages 15–90 that never “level off” and instead changed constantly throughout the adult phase of life (Walhovd et al., 2005). [...] it is unclear whether there is even a steady set-point at all."
- "Dosenbach et al., 2010 used data-driven classification algorithms to compute an estimated “brain age” of individual subjects 7 to 30 years of age based on widespread intrinsic connectivity patterns within and between brain networks [...] However, these data also illustrate the challenges of applying general patterns of neurodevelopment from group-based to individual inference, as there is substantial variance in brain network connectivity that is unrelated to age. For example, some 8-year-old brains exhibited a greater “maturation index” than some 25 year old brains."
- Giedd, J. et al (1999). "Brain development during childhood and adolescence: a longitudinal MRI study," Nature Neuroscience, 2(10):861-3.
- "Pediatric neuroimaging studies, up to now exclusively cross sectional, identify linear decreases in cortical gray matter and increases in white matter across ages 4 to 20. In this large-scale longitudinal pediatric neuroimaging study, we confirmed linear increases in white matter, but demonstrated nonlinear changes in cortical gray matter, with a preadolescent increase followed by a postadolescent decrease. These changes in cortical gray matter were regionally specific, with developmental curves for the frontal and parietal lobe peaking at about age 12 and for the temporal lobe at about age 16, whereas cortical gray matter continued to increase in the occipital lobe through age 20. The subjects for this study were healthy boys and girls participating in an ongoing longitudinal pediatric brain-MRI project at the Child Psychiatry Branch at the National Institute of Mental Health. [...] This MRI study demonstrates a preadolescent increase in cortical gray matter; this phenomenon was previously obscured, probably by the lack of longitudinal data, as even in an analysis of the 145 cross-section-al data points in our sample, the largest to date, we could not detect nonlinearity in these developmental curves".
- Bartzokis, G. et al., (2001). "Age-related changes in frontal and temporal lobe volumes in men: a magnetic resonance imaging study," Arch Gen Psychiatry, Aug; 58(8):774.
- "Methods: Seventy healthy adult men aged 19 to 76 years underwent magnetic resonance imaging. Coronal images focused on the frontal and temporal lobes were acquired using pulse sequences that maximized gray vs white matter contrast. The volumes of total frontal and temporal lobes as well as the gray and white matter subcomponents were evaluated. Results: Age-related linear loss in gray matter volume in both frontal (r = -0.62, P<.001) and temporal (r = -0.48, P<.001) lobes was confirmed. However, the quadratic function best represented the relationship between age and white matter volume in the frontal (P<.001) and temporal (P<.001) lobes. Secondary analyses indicated that white matter volume increased until age 44 years for the frontal lobes and age 47 years for the temporal lobes and then declined. Conclusions: The changes in white matter suggest that the adult brain is in a constant state of change roughly defined as periods of maturation continuing into the fifth decade of life followed by degeneration. Pathological states that interfere with such maturational processes could result in neurodevelopmental arrests in adulthood."
- Del Giudice, M, (2014). "Middle Childhood: An Evolutionary-Developmental Synthesis", Child Development Perspectives, Volume 8, Number 4, Pages 193–200.
- Del Giudice has age 6-8 as the peak for gray matter (see tables). This paper also goes into detail about development in middle-childhood, most importantly the onsent of adrenarche[22] between 6-8 years of age, giving rise to sexual differentiation in behavior - including sexual curiosity and attraction. It could be argued that as a developmental milestone, this age is as important, if not more so than the start of puberty, as determined by thelarche or gonardarche.
- "By age 6, the brain has almost reached its maximum size and receives a decreasing share of the body’s glucose after the consumption peak of early childhood (see Figure 1; Giedd & Rapoport, 2010; Kuzawa et al., in press). However, brain development proceeds at a sustained pace, with intensive synaptogenesis in cortical areas (gray matter) and rapid maturation of axonal connections (white matter; Lebel, Walker, Leemans, Phillips, & Beaulieu, 2008). [...] The most dramatic changes probably occur in the domain of self-regulation and executive functions: Children become much more capable of inhibiting unwanted behavior, maintaining sustained attention, making and following plans, and so forth (Best, Miller, & Jones, 2009; Weisner, 1996)."
- Mousley, A., Bethlehem, R. A. I., Yeh, F. C., & Astle, D. E. (2025). Topological turning points across the human lifespan. Nature communications, 16(1), 10055. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-65974-8
- "[W]e identified four major topological turning points across the lifespan – around nine, 32, 66, and 83 years old."
- “The second lifespan epoch, ages nine to 32, indicates that the trajectory of topological development remains consistent across this period. While adolescence begins with puberty, the end of adolescence is less clear, with older definitions ending before 20 and more recent definitions extending into the mid-20s. The transition to adulthood is influenced by cultural, historical, and social factors, making it context-dependent rather than a purely biological shift. Our findings suggest that in Western countries (i.e., the United Kingdom and United States of America), adolescent topological development extends to around 32 years old, before brain networks begin a new trajectory of topological development.”
Competence
it's widely believed that minors differ fundamentally in their cognitive and decision-making abilities from adults. In addition legal definitions are often conflated with real capacities of people, leading to belief in a clear boundary between competent and incompetent ages. Many studies refuse this view, supporting the concept of evolving capacity.
- Kidd, C (2025) in The Conversation. Children can be systematic problem-solvers at younger ages than psychologists had thought – new research
- "More than half the children we tested demonstrated evidence of structured algorithmic thinking, and at ages as young as 4 years old. While older kids were more likely to use algorithmic strategies, our finding contrasts with Piaget’s belief that children were incapable of this kind of systematic strategizing before 7 years of age. Our results suggest that children are actually capable of spontaneous logical strategy discovery much earlier when circumstances require it. Explaining our results requires a more nuanced interpretation of Piaget’s original data. While children may still favor apparently less logical solutions to problems during the first two Piagetian stages, it’s not because they are incapable of doing otherwise if the situation requires it."
- Johnson SB, Blum RW, Giedd JN. Adolescent maturity and the brain: the promise and pitfalls of neuroscience research in adolescent health policy. J Adolesc Health. 2009 Sep;45(3):216-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.05.016.
- "As of yet, however, neuroimaging studies do not allow a chronologic cut-point for behavioral or cognitive maturity at either the individual or population level. The ability to designate an adolescent as “mature” or “immature” neurologically is complicated by the fact that neuroscientific data are continuous and highly variable from person to person; the bounds of “normal” development have not been well delineated.[...] In sum, neuroimaging modalities involve an element of subjectivity, just as behavioral science modalities do. A concern is that high-profile media exposures may leave the mistaken impression that fMRI, in particular, is an infallible mind-reading technique that can be used to establish guilt or innocence, infer “true intentions,” detect lies, or establish competency to drive, vote, or consent to marriage.[...] Although scientists may be reticent to apply their research to policy, in some cases, policy makers are doing it for them."
- "Ultimately, the goal is to be able to articulate the conditions under which adolescents’ competence, or demonstrated maturity, is most vulnerable and most resilient. Resilience, it seems, is often overlooked in contemporary discussions of adolescent maturity and brain development. Indeed, the focus on pathologic conditions, deficits, reduced capacity, and age-based risks overshadows the enormous opportunity for brain science to illuminate the unique strengths and potentialities of the adolescent brain. So, too, can this information inform policies that help to reinforce and perpetuate opportunities for adolescents to thrive in this stage of development, not just survive."
- Leah H. Somerville. 2016. Searching for Signatures of Brain Maturity: What Are We Searching For? Neuron, 92(6), 1164–1167, doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.059
- "A key principle that guides determinations about psychological maturity in adolescence and young adulthood is the degree to which contextual factors shape an individual’s behavior. For instance, an adolescent and an adult could achieve an identical level of performance on a cognitive task under certain conditions—say, when free of distraction and when the situation has low emotional arousal. However, if the context is shifted slightly by embedding reward cues in the cognitive task, adolescents’ performance disproportionally shifts compared to adults (e.g., Somerville et al., 2011). [...] A prime example of context-sensitive policy is graduated driving laws. They initially constrain new drivers to highly regulated conditions (e.g., during the day, without peers in the car) and slowly broaden the range of driving contexts as new drivers gain experience."
- "one consequence of this framework would be the need to abandon the goal of identifying a single age-of-brain maturity. Rather, there would be a suite of maturity points that reflect different neural systems and different associated behaviors. For example, an individual could reach an age of “baseline cognitive maturity”—the capacity to engage in goal-directed behavior under neutral, non-distracted circumstances, substantially earlier than an age of “cognitive-emotional maturity”—the capacity to maintain goal-directed behavior in the face of competing emotional cues."
- Epstein, Robert (2010). chapter "Adultness" in"Teen 2.0", 148-157.
- "After reviewing the relevant scientific literature, interviewing many adults, and consulting with three other psychologists and two psychiatrists with expertise in adult development issues, we concluded that there are fourteen different skill-sets or "competencies" [love, sex, leadership, problem solving, physical abilities, verbal and math, interpersonal skills, responsibility, managing high-risk behaviors, work, education, personal care, self-management, and citizenship] that distinguish adults from non-adults. [...] For three of the competencies--love, leadership and problem solving--we did find statistically significant differences between the mean scores of teens and adults, with adults outscoring the teens. But the absolute differences were small. [...] On two other scales--work and self-management--the differences between the adult scores and teen scores were marginally significant (at the .05 level), again in the adults' favor, but the absolute differences were less than 4 percent. On the other nine scales, we found no significant differences at all between the adult and teen scores. [...] fifty five of the adults in our sample were college graduates--more than double the rate of college graduates in the United States."
- Epstein, Robert (2007). "The Myth of the Teen Brain," Scientific American Mind, April/May, 57-63.
- "Visual acuity, for example, peaks around the time of puberty. "Incidental memory"—the kind of memory that occurs automatically, without any mnemonic effort, peaks at about age 12 and declines through life. [...] In the 1940s pioneering intelligence researchers J. C. Raven and David Wechsler, relying on radically different kinds of intelligence tests, each showed that raw scores on intelligence tests peak between ages 13 and 15 and decline after that throughout life. Although verbal expertise and some forms of judgment can remain strong throughout life, the extraordinary cognitive abilities of teens, and especially their ability to learn new things rapidly, is beyond question. And whereas brain size is not necessarily a good indication of processing ability, it is notable that recent scanning data collected by Eric Courchesne and his colleagues at the University of California, San Diego, show that brain volume peaks at about age 14."
- "A variety of research in several fields suggests that teen turmoil is caused by cultural factors, not by a faulty brain. [...] Anthropological research reveals that teens in many cultures experience no turmoil whatsoever and that teen problems begin to appear only after Western schooling, movies and television are introduced. [...] Teens have the potential to perform in exemplary ways, the author says, but we hold them back by infantilizing them and trapping them in the frivolous world of teen culture."
- "Studies of intelligence, perception and memory show that teens are in many ways superior to adults. [...] When we treat teens like adults, they almost immediately rise to the challenge."
- Moshman, David (2011). "Adolescent Rationality and Development: Cognition, Morality, and Identity, Third Edition.
- (Intro) "Adolescents are qualitatively and categorically distinct from children. There is no empirical support, however, for a state of rationality or maturity common to most adults, rately seen in adolescents. Even young adolescents often show forms and levels of rationality beyond the competence of many adults, and adults of all ages often fall short of rational standards met by many adolescents [...] it is not surprising to find that in most societies for most of human history there was no such thing as adolescence, at least as we understand it (Epstein, 2007; Grotevant, 1998; Hine, 1999)."
- "Postchildhood developmental changes in thinking are not tied to age and do not culminate in a state of maturity. Although it seems likely that many individuals show progress beyond childhood in the quality of their problem solving, decision making, judgment, and planning (Cauffman & Woolard, 2005; Steinberg & Scott, 2003), the deployment and progress of thinking in adolescence and beyond is highly variable, depending on specific interests, activities, and circumstances (Fischer, Stein, & Heikkinen, 2009). No theorist or researcher has ever identified a form or level of thinking routine among adults that is rarely seen in adolescents. Adolescent thinking often develops but not through a fixed sequence and not toward a universal state of maturity [...] It seems almost irresistible for adults to see themselves as having achieved a state of maturity that adolescents (and even younger adults) have not yet reached, but brain research provides no evidence to support the postulation of advanced states of maturity attained by the most or all adults but few adolescents. Many people continue to develop long beyond childhood, and their brains reflect those changes, but beyond age 12, there is no natural and universal state of maturity waiting to be achieved."
- "Developmental changes beyond age 12 to 14 are much too stable and individualized, it appears to me, for a developmental panel, even if it included brain experts, to succeed in distinguishing age groups on the basis of their age development. Second, there is the reductionist fallacy. Brain data seem more scientific than behavioral data, but they are not, nor do they provide us with ultimate explanations, even if psychology can in principle be reduced to biology, a dubious proposition, we are a very long way from achieving such a reduction."
- Editor: Moshman then published an article in HuffPo, that explains his position.
- Waber, D.P., et al. (2007). "The NIH MRI Study of Normal Brain Development: Performance of a Population Based Sample of Healthy Children Aged 6 to 18 Years on a Neuropsychological Battery," Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 13(5), 729-746.
- "Perhaps most intriguing are the age-related trajectories for raw score performance. For most tasks, proficiency improved dramatically between 6 and 10 years of age, leveling off during early adolescence (approximately 10 to 12 years of age), suggesting that for many neurocognitive tasks, children approach adult levels of performance at that age. For a few measures, scores increased linearly throughout the age range. These were tasks that assessed basic information processing, such as Coding, Digit Span, and Spatial Span. Still others were associated with a non-linear component during adolescence. Some showed a flattening of the curve followed by another period of acceleration, suggesting another spurt in mid-adolescence. Verbal learning actually reversed direction with performance declining in later adolescence."
- Adler, N.E., & Matthews, K. (1994). "Health Psychology: Why do Some People Get Sick and Some Stay Well?," Annual Review of Psychology, 45, 229-259.
- "However, empirical tests show that adolescents are no less rational than adults. Applications of rational models to adolescent decision-making show that adolescents are consistent in their reasoning and behavior after the salient set of beliefs is assessed (Adler et al 1990). Quadrel et al (1993) demonstrated that adolescents are no more biased in their estimates of vulnerability to adverse health outcomes than are their parents."
- Weithorn, L. A. & Campbell, S. B. (1982). "The competency of children and adolescents to make informed treatment decisions," Child Development, 53(6), 1589-1598.
- "In general, minors aged fourteen were found to demonstrate a level of competence equivalent to that of adults. [...] The ages of eighteen or twenty-one as the "cutoffs" below which individuals are presumed to be incompetent to make determinations about their own welfare do not reflect the psychological capabilities of most adolescents."
- Offer, D. (1987). "In defense of adolescents," Journal of the American Medical Association, 257, 3407-3408.
- Mike Males describes this study: "Northwestern University psychiatrist Daniel Offer, the nation’s leading researcher on adolescents, studied 30,000 teenagers and adults from the 1960s to the 1990s. He and his colleagues found 85% to 90% of teens held attitudes and risk perceptions similar to that of their parents, were not alienated, did think about the future, were coping well with their lives, and did not display psychological disturbances. "Decision making for adults is no different than decision making among teenagers,” Offer reported in 1987 in the Journal of the American Medical Association."
- Offer, D., and Schonert Reichl, K.A. (1992). "Debunking the myths of adolescence: Findings from recent research," Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 31, 1003 1014.
- "[T]he effects of pubertal hormones are neither potent nor pervasive (Brooks-Gunn and Reiter, 1990). [...] Adolescence does not occur in a vacuum and is significantly affected by the sociocultural context in which it occurs. A recent investigation by Enright et al. (1987) illustrates this point. This study was based on the careful reading of 89 articles in the Journal of Genetic Psychology for the past 100 years. The articles were rated for their conceptions about the nature of adolescence. Enright et al. demonstrated ideological bias in approaches to understanding adolescent psychology, specifically in relation to economic conditions. Specifically, in times of economic depression, theories emerged in the literature that portrayed adolescents as "immature, psychologically unstable, and in need of prolonged participation in the education system" (p. 553). In contrast, during wartime, the psychological competence of adolescents was accentuated. The authors point out, "The field of adolescent psychology is not free from the societal influences that impinge upon legislators, educators, and parents in shaping American adolescents" (p. 554)."
- Quadrel, M. J., Fischhoff, B., & Davis, W. (1993). "Adolescent (in)vulnerability," American Psychologist, 48, 102-116.
- "Three groups of subjects were asked to judge the probability that they and several target others (a friend, an acquaintance, a parent, a child) would experience various risks. Subjects were middle-class adults, their teenage children, and high-risk adolescents from treatment homes. All three groups saw themselves as facing somewhat less risk than the target others. However, this perception of relative invulnerability was no more pronounced for adolescents than for adults. Indeed, the parents were viewed as less vulnerable than their teenage children by both the adults and those teens. These results are consistent with others showing small differences in the cognitive decision-making processes of adolescents and adults. Underestimating teens' competence can mean misdiagnosing the sources of their risk behaviors, denying them deserved freedoms, and failing to provide needed assistance."
- Hershovitz, S. (2022). "Why Kids Make the Best Philosophers," The Atlantic.
- "According to Piaget, Sarah should have been in the preoperational stage of development, so called because kids in it can’t yet use logic. But Sarah’s logic was exquisite—far more compelling than the cosmological argument. Whatever you make of an infinite regress of causes, it’s hard to imagine an infinite regress of cats. Matthews decided to study kids and their capacity for philosophical thought, introducing many people to the idea that kids are serious thinkers. Over decades of conversations with children, he found that “spontaneous excursions into philosophy” were common from the ages of 3 to 7. And he was struck by the subtle ways in which kids reasoned, as well as the frequency with which they surfaced philosophical questions. [...] Developmental psychologists are catching on to kids’ capabilities. Nowadays, most of them reject the idea that kids’ minds improve as they age. In The Philosophical Baby, Alison Gopnik writes, “Children aren’t just defective adults, primitive grownups gradually attaining our perfection and complexity.” Their minds are different, but “equally complex and powerful.” Child development, she says, is “more like a metamorphosis, like caterpillars becoming butterflies, than like simple growth—though it may seem that children are the vibrant, wandering butterflies who transform into caterpillars inching along the grown-up path.”."
- Siegel, D. J. (2014). "Pruning, Myelination, and the Remodeling Adolescent Brain," Psychology Today.
- Editor: Dr Siegel appears to believe in some of the myths surrounding the adolescent brain. He points to Synaptic Pruning, which has been suggested as one explanation for the fall in gray matter during the teen years, but his inference is not of much help to ageists who seek to withhold responsibilities from young people: "The classic “use it or lose it” principle applies to adolescence—those circuits that are actively engaged may remain, those underutilized may be subject to systematic destruction. And so for an adolescent, this means that if you want to learn a foreign language well, play a musical instrument, or be proficient at a sport, engaging in those activities before and during adolescence would be a good idea. We move from open potential in childhood to specialization during and following adolescence."
- Del Giudice M. (2014) Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. Handbook of Life Course Health Development. Cham (CH): Springer; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3
- "In biological terms, middle childhood corresponds to human juvenility — a stage in which the individual is still sexually immature, but no longer dependent on parents for survival. In social mammals and primates, juvenility is a phase of intense learning — often accomplished through play — in which youngsters practice adult behavioral patterns and acquire essential social and foraging skills."
- "The transition to middle childhood is marked by a simultaneous increase in perceptual abilities (including a transition from local to global visual processing), motor control (including the emergence of adult-like walking), and complex reasoning skills (Bjorklund, 2011; Poirel et al., 2011; Weisner, 1996)."
- "However, children at this age are not just learning and playing. Cross-culturally, middle childhood is the time when children are expected to start helping with domestic tasks—such as caring for younger siblings, collecting food and water, tending animals, and helping adults prepare food (Bogin, 1997; Lancy & Grove, 2011; Scalise Sugiyama, 2011; Weisner, 1996). In favorable ecologies, juveniles can contribute substantially to family subsistence (Kramer, 2011). Thanks to marked increases in spatial cognition (reflected in the emerging ability to understand maps) and navigational skills, children become able to memorize complex routes and find their way without adult supervision (Bjorklund, 2011; Piccardi, Leonzi, D’Amico, Marano, & Guariglia, 2014)."
- "On a broader social level, cross-cultural evidence shows that juveniles start “getting noticed” by adults—that is, they begin to be viewed fully as people with their own individuality, personality, and social responsibility (Lancy & Grove, 2011)."
- "While children are still receiving sustained investment from parents and other relatives—in the form of food, protection, knowledge, and so forth—they also start to actively contribute to their family economy. By providing resources and sharing the burden of child care, juveniles can boost their parents’ reproductive potential. The dual nature of juveniles as both receivers and providers explains many psychological features of middle childhood and has likely played a major role in the evolution of human life history (Kramer, 2011)."
- Lancy, D. F., & Grove, M. A. (2011). Getting noticed: Middle childhood in cross-cultural perspective. Human Nature, 22, 281-302.
- "Naming and other rites of passage sometimes acknowledge this transition, but it is, reliably, marked by the assumption or assignment of specific chores or duties.[...] There is also an acknowledgement at the exit from middle childhood, of near–adult levels of competence — as a herdsman or hunter or as gardener or infant-caretaker."
- "In Jean Piaget’s influential theory of human cognitive development, the period from 5 to 7 years is marked by a major transition from pre-operational to concrete operational thinking (Piaget 1963). From a historical standpoint there is a great deal of evidence that this age range also marked a major transition in children’s social standing, in particular that a 7 year-old could be held legally and morally accountable for his/her actions (White 1991: 13)."
- "The last point we would make is that the various markers of the onset of middle childhood we have enumerated all seem to be tied to a shift in cognitive functioning. There is an evident sensitivity to the expectations and needs of others—critical in child-minding and errand running. The child displays other indicators of “sense,” including lengthened attention span, greater language facility, and persistence in completing tasks. He or she is a willing student. The manifold signs of awareness of appropriate behavior vis-à-vis sex and gender go along with increased complexity in peer relations and rule-governed play. On the other hand, the exit from middle childhood is signaled more by markers of physical maturity—including secondary sexual characteristics, a growth spurt, voice change, increased sexuality, and augmented strength and endurance."
- Wang, F., Tong, Y., & Danovitch, J. (2019). Who do I believe? Children’s epistemic trust in internet, teacher, and peer informants. Cognitive Development, 50, 248–260. Doi:10.1016/j.cogdev.2019.05.006
- "Taken together, our findings suggest that school age children can reason about the reliability of information sources from different categories and that their judgments are sensitive to the type of information being sought. Just as children can be skeptical when making judgments about the reliability of different people (see Mills, 2013), children’s belief in information from the internet is not immutable. "
Informed consent
Children's decision-making ability has recently come under scrutiny, with consent to clinical research,[23] gender transition and vaccination efforts the most common contemporary themes so far. In a paper that repeated some of the myths re. development of older teens, it was nevertheless held that for children over the age of 11.2 need not be assessed individually for their ability to give consent to take part in clinical research.
- Hein, M. et al, (2015). "Informed consent instead of assent is appropriate in children from the age of twelve," BMC Medical Ethics, 2015, 16:76.
- "Children between 9.6 and 11.2 years were in the change-over period, an individual assessment of competence might be applicable in this age group. Children of 11.2 years and above can generally be considered decision-making competent, and although they need a supportive context, no individual assessment is needed."
Child's competence in law
- Lauren Eade (2001) Legal Incapacity, Autonomy, and Children's Rights, Newcastle Law Review 5, (a copy)
- Doli incapax [age of criminal responsibility] and age of consent laws are representative of the two ways in which the law's presumption of children's incapacity denies autonomy even to the actually competent child. One denies autonomy and the fundamental stage of formation of intent; the other refuses to acknowledge the validity of a child's intent in particular areas. Both are devoid of scientific basis. Both are motivated by questionable control motives as well as a desire to protect. And both conceptualise the child in a manner inherently incompatible with the child as rights-holder.
- But incapacity does not have to be an "all or nothing" issue. There is no reason why incapacity in some areas should deny capacity and autonomy in others, or why a child cannot be protected as well as allowed rights appropriate to his or her level of development. These are only irreconcilable propositions in the current model that presumptively ascribes incapacity to all children. If the law were to abandon its over-protective prejudices and engage with each child individually, judging his or her actual competence, these unjust consequences would be avoided. Immature children could retain the protection of incapacity. Specifically or generally autonomous children could gain recognition of their rights. And the law could at last acknowledge the fundamental fact that each and every child is a distinctly different human being.
Risk Taking/Impulsivity/Prefrontal Physiology
The oft-repeated myth of the human brain maturing fully at 25, is simplistic and outdated. If impulse control were dependent upon prefrontal volume, we would see no such thing as the quiet, studious preschooler - as all preschoolers have a tiny prefrontal cortex. As the previous studies suggest, the brains of teenagers are already losing gray matter and raw processing power is already declining by that age. Further studies are now informing us that functions of the prefrontal cortex are borrowed from other parts of the brain in teens, and raw levels of impulse-control are equal to or greater than that of adults. However, teens and young adults in particular, might be slightly less discriminatory, and less likely to use cognitive control when facing tasks within a negative emotional context. While this might manifest in poorer performance within an experimental context, it is likely to be an adaptive (possibly pro-reproductive) trait that is net beneficial to socialization/competence building during youth, or otherwise experimental evidence of inadequate socialization. Further, there is no sound evidence to support the idea that the amygdala is the brain's "fear center"[24] - so any differences in teens' amygdala response can not be traced to function, let alone be ascribed to a mental deficiency. One would also have to account for the fact that when compared to adults, smaller childrens' level of amygdala activation is similar to that of adults, unlike teens. With respect to risk-taking sexual behavior, younger teens are no less careful than older adolescents, however, there are ethnic/cultural differences which prohibitionists appear to ignore.
- Kolk, S.M., Rakic, P. (2022). Development of prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacol. 47, 41–57. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01137-9
- "The constantly developing cognitive and executive capabilities occur parallel to the neurophysiological changes within the PFC and its connected areas and seem to reach a plateau in teenagers (around 12 years in human, around P50 in rodents)"
- Steinberg, L., (2008). "A Social Neuroscience Perspective on Adolescent Risk-Taking," Developmental Review, Volume 28, Issue 1, March 2008, Pages 78-106.
- "Among the widely-held beliefs about adolescent risk-taking that have not been supported empirically are (a) that adolescents are irrational or deficient in their information processing, or that they reason about risk in fundamentally different ways than adults; (b) that adolescents do not perceive risks where adults do, or are more likely to believe that they are invulnerable; and (c) that adolescents are less risk-averse than adults. None of these assertions is correct: The logical reasoning and basic information-processing abilities of 16-year-olds are comparable to those of adults; adolescents are no worse than adults at perceiving risk or estimating their vulnerability to it (and, like adults, overestimate the dangerousness associated with various risky behaviors); and increasing the salience of the risks associated with making a poor or potentially dangerous decision has comparable effects on adolescents and adults (Millstein & Halpern-Felsher, 2002; Reyna & Farley, 2006; Steinberg & Cauffman, 1996; see also Rivers, Reyna, & Mills, 2008, this issue). Indeed, most studies find few, if any, age differences in individuals’ evaluations of the risks inherent in a wide range of dangerous behaviors (e.g., driving while drunk, having unprotected sex), in their judgments about the seriousness of the consequences that might result from risky behavior, or in the ways that they evaluate the relative costs and benefits of these activities (Beyth-Marom, Austin, Fischoff, Palmgren, & Jacobs-Quadrel, 1993). In sum, adolescents’ greater involvement than adults in risk-taking does not stem from ignorance, irrationality, delusions of invulnerability, or faulty calculations (Reyna & Farley, 2006)."
- Casey, B., (2013). "The Teenage Brain: Self Control," Current Directions in Psychological Science, Volume: 22 issue: 2, page(s): 82-87.
- "Adolescence, by definition, involves new demands on the individual as she or he moves from dependence on the family unit to relative independence. This developmental period is not specific to humans, as evidenced by the increases in novelty seeking, interactions with peers, and fighting with parents observed in other species (see Romeo, 2013; Spear, 2013; both in this issue). These behaviors are thought to have evolved to serve adaptive functions related to successful mating and obtainment of resources necessary for survival (Spear & Varlinskaya, 2010). [...] To suggest that this period of development is one of no brakes or steering wheel (Bell & McBride, 2010) is to greatly oversimplify it. [...] Self-control—in this case, suppressing a compelling action—showed a different developmental pattern in the context of emotional information than in its absence, especially for males (Tottenham, Hare, & Casey, 2011). As illustrated in Figure 1 (also see Fig. 1 in Hare et al., 2008; National Research Council, 2011), when no emotional information is present, not only do many adolescents perform as well as adults, some perform even better. However, when decisions are required in the heat of the moment (i.e., in the presence of emotional cues; Fig. 2a), performance falters (Fig. 2b). Specifically, adolescents have difficulty suppressing a response to appetitive social cues relative to neutral ones. [...] Recently, a number of human imaging studies have attempted to evaluate this model and test for unique patterns of brain activity in adolescents during stereotypical risky behavior in the context of incentives (Chein, Albert, O’Brien, Uckert, & Steinberg, 2011; J. R. Cohen et al., 2010; Geier, Terwilliger, Teslovich, Velanova, & Luna, 2010; Van Leijenhorst et al., 2010). This work has challenged the view that diminished self-control in adolescents is due to a less mature prefrontal cortex that leads to less successful exertion of regulatory control on behavior (Bell & McBride, 2010). [...] Indeed, if the objective of adolescence is to gain independence from the family unit, then providing opportunities for adolescents to engage in new responsibilities is essential. Without opportunities and experiences to help optimally shape the adolescent’s brain and behavior, the objectives of this developmental phase will not easily be met."
- Mills, K. L., Goddings, A.-L., Clasen, L. S., Giedd, J. N., & Blakemore, S.-J. (2014). The Developmental Mismatch in Structural Brain Maturation during Adolescence. Developmental Neuroscience, 36(3-4), 147–160.
- "The majority of individuals in our sample showed relatively earlier maturation in the amygdala and/or NAcc compared to the PFC, providing evidence for a mismatch in the timing of structural maturation between these structures. We then related individual developmental trajectories to retrospectively assessed self-reported risk-taking and sensation-seeking behaviors during adolescence in a subsample of 24 participants. Analysis of this smaller sample failed to find a relationship between the presence of a mismatch in brain maturation and risk-taking and sensation-seeking behaviors during adolescence. Taken together, it appears that the developmental mismatch in structural brain maturation is present in neurotypically developing individuals. This pattern of development did not directly relate to self-reported behaviors at an individual level in our sample, highlighting the need for prospective studies combining anatomical and behavioral measures."
- Bronski, J. (2021). "An Empirical Introduction to Youth"
- "The 2010 study looked at, among many, a white matter tract called the “uncinate fasciculus [which] … is a large fiber track connecting three key regions involved in emotion regulation: [the] amygdala, lateral and medial prefrontal cortex”136. This connection, which considering the evidence is safely considered to be done with all meaningful structural development by the end of puberty (which is likely to be before the age of fifteen), is exactly what some scientists claim causes a functional difference in teens. Specifically, they claim, among other things, that in teens the amygdala struggles to communicate with the frontal lobe, leading to lower inhibition of primal amygdalic functions. There is no evidence for this claim, since we have seen that the uncinated fasciculus, the main track connecting the amygdala and the frontal lobe, is mature at the end of puberty. So far we have seen that gray matter, in the prefrontal cortex and the rest of the brain, is accumulated until puberty, when it begins to be pruned. This pruning will continue into old age; there is nothing significant about the age of 25 when it comes to loss of gray matter. We have also seen that the accumulation of white matter reaches its peak rate at the age of one year, and continues at decreasing rates until the age of approximately 45, in the prefrontal cortex and elsewhere in the brain. There is nothing significant about the age of 25 when it comes to the accumulation of white matter. Finally, in direct contrast to the unscientific claim that “Adults think with the prefrontal cortex, the brain’s rational part … Teens process information with the amygdala,” teens do in fact have working prefrontal cortexes, and the connections between that part of the brain and the amygdala are mature by the end of puberty. There is nothing significant about the age of 25 when it comes to the connection between the hindbrain and the forebrain, or the extent to which one “thinks” with either part of the brain. How do we now judge the statement that “The rational part of a teen’s brain isn’t fully developed and won’t be until age 25 or so?” Poorly. The proposition is clearly unsupported by the data regarding structural changes in the brain. Based on what we have reviewed, the claim seems totally arbitrary. Let us be charitable and look for other evidence that (Landouceur et al. 2012) might comment on this view. Perhaps the function of the brain only reaches mature levels at the age of 25. Development of Organ Function Function is what matters. For whatever reason, teen-brain neuroscientists love to obscure the debate on the maturity of the “teen brain” by making claims about its supposed structural immaturities. As we have seen, the actual evidence for these immaturities is sparse at best. Many claims of structural and functional immaturity rest on young, physically immature participants, which are grouped with older teens. Claims are then extended to all teenagers and hyperbolized in the news cycle. For instance, Dr. Giedd, who co-authored the 2004 gray matter study, has gone on the news and made claims about the immaturity of the brain “through adolescence.” The definition of adolescence is, of course, slippery. His data shows structural maturity by the age of 14 or 15, which he vaguely refers to as “late adolescence.” The WHO then defines adolescence as occurring during the ages 10-19. Many in the news refer to the age of 25 as the specific age at which the brain reaches maturity. How this came about has already been hinted at: earlier, a source was reviewed which showed that myelination of the frontal lobes continues until the mid-forties. One scientist, BJ Casey, ran an experiment which only featured participants up to the age of 24-25, and found that myelination continued to the highest age featured in the study. Out of this came the claim that the brain is still developing until the age of 25. In reality, further data shows that by this metric, the brain develops until 45! Dr. Frances Jensen wrote a whole book on this misleading claim, saying in a promotion article published in Time, The myelination process starts from the back of the brain and works its way to the front. That means the prefrontal cortex, the area of the brain involved in decisionmaking, planning and self-control, is the last part to mature. It’s not that teens don’t have frontal- lobe capabilities but rather that their signals are not getting to the back of the brain fast enough to regulate their emotions. It’s why risk-taking and impulsive behavior are more common among teens and young adults. “This is why peer pressure rules at this time of life,” says Jensen. “It’s why my teenage boys would come home without their textbook and realize at 8 p.m. that they have a test the next day. They don’t have the fully developed capacity to think ahead at this time.” She also claims in her book that the teenage brain is “only 80% developed,” without a source."
- Romer, D. (2010). "Adolescent Risk Taking, Impulsivity, and Brain Development: Implications for Prevention," Developmental Psychobiology, 52(3): 263–276.
- "A review of the evidence for the hypothesis that limitations in brain development during adolescence restrict the ability to control impulsivity suggests that any such limitations are subtle at best. Instead, it is argued that lack of experience with novel adult behavior poses a much greater risk to adolescents than structural deficits in brain maturation [...] The evidence we have reviewed suggests that adolescent risk taking is not a universal phenomenon and that individual differences related to at least three types of impulsivity underlie such behavior in adolescents. Furthermore, at least two forms of impulsivity are associated with weak executive function as assessed by working memory and response inhibition tasks. However, sensation seeking does not appear to be inversely related to either of these executive functions and may actually be somewhat positively related to working memory ability."
- Romer, D. et al, (2017). "Beyond stereotypes of adolescent risk taking: Placing the adolescent brain in developmental context," Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, Volume 27, Pages 19-34.
- Editor: For more on Romer's interpretation, see his article in Smithsonian Magazine.
- "In conclusion, we have presented an alternative model of adolescent brain development that emphasizes the accumulation of experience as adolescents age and transition to adulthood, with concomitant changes in judgment and decision making (see Table 1 for a summary of differences between the Life-span Wisdom Model and Imbalance Models). The model explains much of the apparent increase in adolescent risk taking as an adaptive need to gain the experience required to assume adult roles and behaviors. The risk-taking that reflects lack of control or excessive sensitivity to immediate rewards is primarily an individual difference that characterizes some persons from an early age that can persist well into adulthood. At the same time, the adolescent brain is supremely sensitive to the learning that can occur during this period and has cognitive capacities to take advantage of the experience gained. The result is a brain with integrated circuits encompassing executive function (i.e., cognitive control and inhibition), as well as verbatim and gist memory networks, which can be called upon to negotiate both novel and familiar situations. The preservation of robust gist thinking maintains wise decision making during later adulthood when cognitive control capacities diminish. We believe this approach is more aligned with the scientific evidence, including results that challenge stereotypes about the adolescent brain."
- Khurana, A., Romer, D., Betancourt, L. M., Brodsky, N. L., Giannetta, J. M., & Hurt, H. (2015). Stronger Working Memory Reduces Sexual Risk Taking in Adolescents, Even After Controlling for Parental Influences. Child Development, 86(4), 1125–1141.
- "Of those who had initiated sexual activity by T3 (n = 91), nearly one in every four adolescents (27.5%) reported not using a condom during their last sexual intercourse. Significant age differences were observed in the rates of sexual initiation, with older adolescents more likely to have initiated intercourse (t = 5.14, p < .001). No age differences were observed in condom use among those who had initiated sexual intercourse. Similarly, we noted no gender differences in the rates of sexual initiation or condom use in our sample. In terms of racial-ethnic variations, Black and Hispanic youth were more likely to have initiated sexual intercourse at T2 and T3, as compared to non-Hispanic White, Asian, and Native American youth. Black (34.5%) and Hispanic (46.2%) youth also had relatively higher rates of condom nonuse as compared to White youth (18.7%) in the nonvirgin subsample at T3."
- Moshman, David (2011). "Adolescent Rationality and Development: Cognition, Morality, and Identity, Third Edition.
- "There is no evidence that adolescents are uniquely egocentric or even much different from adults in this regard; on the contrary, research has shown age differences to be minimal or nonexistent (Millstein & Halpern-Felsher, 2002; Quadrel et al., 1993; Smetana & Villalobos, 2009). As fo the specific assertion that adolescents see themselves as invulnerable, it appears instead that adolescents routinely, and often drastically, overestimate their actual vulnerability (Millstein & Halpern-Felsher, 2002). [...] risk taking is not always bad, and adolescents are not uniquely prone to it. People of all ages take risks of all sorts, including foolish and dangerous risks; there is no empirical basis for the common assumption that risk taking is a special phenomenon of adolescence. On the contrary, direct comparisons of adolescents and adults show minimal age differences (Beyth-Marom et al., 1993). Sociological data indicate that when covariates such as poverty are controlled, adolescents are no more prone to risk taking than adults, who in fact take plenty of dubious risks (Males, 2009, 2010)."
- Males, M. (2009). "Does the Adolescent Brain Make Risk Taking Inevitable?" Journal of Adolescent Research, 24(1), 3–20.
- "Far from justifying antiprecocity measures, emerging brain science, viewed in social contexts, indicates the dangers of efforts to restrict youth and to banish them from adult behaviors and public spaces. Preliminary analyses of brain physiology suggest that “taking risks is precisely the experience that develops the pre frontal cortex . . . you don’t learn what you need for adulthood by being excluded from it until you can demonstrate that you have got the right circuits” (Sercombe, in press). Viewed as a system, American social and health policies built on age-segregating measures may well be contributors to the extraordinarily high-risk behaviors prevailing among American youths and adults well into middle age compared with their counterparts in peer nations. There may be a price to pay in the adaptability of larger society as well. If brain science is to be credited with biodeterminist findings, neuroscannings and cognitive tests reveal developments in the middle-aged brain that make worry over teenage brains look silly. Significant losses in key memory and learning genes (Lu et al, 2004), mental fluidity (Schaie & Willis, 2008), and measurable losses in IQ show up in middle age and accelerate in senior years. Although some research indicates that myelinization (the pruning and selection of certain cerebral nerve fibers for myelin sheathing) aids adult brains in handling familiar situations more efficiently, it also renders them less able to address new challenges than more flexibly circuited younger brains."
- Del Giudice M. (2014) Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. Handbook of Life Course Health Development. Cham (CH): Springer; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3
- "The most dramatic changes probably occur in the domain of self-regulation and executive functions: children become much more capable of inhibiting unwanted behavior, maintaining sustained attention, making and following plans, and so forth (Best, Miller, & Jones, 2009; Weisner, 1996)."
- Berns GS, Moore S, Capra CM (2009) Adolescent Engagement in Dangerous Behaviors Is Associated with Increased White Matter Maturity of Frontal Cortex. PLoS ONE 4(8): e6773. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006773
- "The direction of correlation suggests that rather than having immature cortices, adolescents who engage in dangerous activities have frontal white matter tracts that are more adult in form than their more conservative peers."
Moral reasoning
- Haidt, J. (2001). "The emotional dog and its rational tail: A social intuitionist approach to moral judgment," Psychological Review, 108, 814-834.
- "Turiel (1983) has shown that young children do not believe [that actions are wrong just because they are punished]. They say that harmful acts, such as hitting and pulling hair, are wrong whether they are punished or not. They even say that such acts would be wrong if adults ordered them to be done."
- Del Giudice M. (2014) Middle childhood: an evolutionary-developmental synthesis.; 8:193–200. doi:10.1111/cdep.12084. in: Halfon N, Forrest CB, Lerner RM, et al., editors. Handbook of Life Course Health Development. Cham (CH): Springer; 2018. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47143-3
- "Parallel improvements take place in mentalizing (the ability to understand and represent mental states) and moral reasoning, as children become able to consider multiple perspectives and conflicting goals (Jambon & Smetana, 2014; Lagattuta, Sayfan, & Blattman, 2009)."
Excerpt Graphic Library
The EGL on Competences and Development has some relevant information. Just right click/save and reproduce by uploading in short-form media to bypass character limits.
-
Basic brain aging primer
-
Teen Brain research summary
-
Age chauvinism
-
BJ Casey
-
Joseph Bronski
-
Full Brain Size and adult-like competences in early childhood
-
Development of reasoning ability in early childhood (Moshman, 2005)
-
Early development of brain - Del Giudice
-
White and Gray Matter levels - Del Giudice (2017)
-
Bethlehem et al, 2022, brain volumes and matter levels by age
-
Giedd 1999 brain matter curves by age
-
Mills et al: Adolescent brains indistinguishable from adult. Variance in gray matter between individuals is far greater than any changes over time.
-
John Raven - Intelligence hits a peak in the mid teens, then plateaus and declines (the decline may have been at least in part due to poorer education in the interwar period).
-
John Raven - Intelligence hits a peak in the mid teens, then plateaus (note improvement in scores obtained in the 1970s)
-
Moshman on common fallacies of teen brain development
-
Moshman continued
-
Moshman continued
-
Laurence Steinberg (2008)
-
Epstein reviewed, plus other references - raw intelligence peak 13-15 y/o
-
2020 meta-analysis on the age of Thelarche (breast budding in girls - start of puberty). Similar for first period.
-
Conclusions of the aforementioned 2020 meta-analysis
-
Physical development - Tanner stages reached considerably earlier than commonly supposed
-
Physical development - Ages of pubertal development lower than commonly stated
-
Girls developing sexual features almost completely by 11
See also
- Perspectives on Ageism include the similarity between "troubled teen industry" literature and scientific racism.
- The concept of Evolving capacity
External links
- Dr. Howard R. Bernstein - Myth of the Adolescent Brain (Video link)
- Jane C. Hu, The Myth of the 25-Year-Old Brain (Slate, Nov 27 2022).
References
- ↑ Slate: Updated take on the 25y/o brain myth
- ↑ Brain research advances help elucidate teen behavior
- ↑ Does The Brain Really Mature At The Age Of 25?
- ↑ Sexual Differentiation of the Human Brain A Historical Perspective
- ↑ The History of Female Brain Studies Reveal a Lot - WSJ
- ↑ The ‘female’ brain: why damaging myths about women and science keep coming back in new forms
- ↑ The Trouble with Sex Differences
- ↑ Dump the “dimorphism”: Comprehensive synthesis of human brain studies reveals few male-female differences beyond size
- ↑ SOME RACIAL PECULIARITIES OF THE NEGRO BRAIN
- ↑ Goldstein HW, Yusko KP, Scherbaum CA, Larson EC. Reducing Black-White Racial Differences on Intelligence Tests Used in Hiring for Public Safety Jobs. J Intell. 2023 Mar 28;11(4):62. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence11040062. PMID: 37103247; PMCID: PMC10143281.
- ↑ BBC - People don't become 'adults' until their 30s, say scientists, Adolescence lasts until 30s
- ↑ APA's Roper Amicus
- ↑ Hodgson (Teen Abortion) Amicus
- ↑ Nature: Can brain scans reveal behaviour? Bombshell study says not yet
- ↑ Scientists Admit Controversial Conflict Casts Doubt On Studies Using Brain Scans
- ↑ There’s a lot of junk fMRI research out there. Here’s what top neuroscientists want you to know - Vox
- ↑ Controversial science of brain imaging - Scientific American
- ↑ Brain Overclaim Syndrome and Criminal Responsibility: A Diagnostic Note
- ↑ MacArthur Foundation: Research Network on Adolescent Development
- ↑ Cabana T, Jolicoeur P, and Michaud J (1993) Prenatal and postnatal growth and allometry of stature, head circumference, and brain weight in Quebec children. Am. J. Hum. Biol.5:93–99.
- ↑ Brain charts for the human lifespan - Bethlehem et al (2022)
- ↑ Gilbert Herdt and Martha McClintock, Ph.D, The Magical Age of 10, in Archives of Sexual Behavior, Vol. 29, No. 6, 2000.
- ↑ Encouraging greater empowerment for adolescents in consent procedures in social science research and policy projects (2023)
- ↑ Visser et al: Robust BOLD responses to faces but not to conditioned threat: challenging the amygdala’s reputation in human fear and extinction learning