One of our staff members is contributing considerably to a News Archiving service at Mu. Any well educated (Masters, PhD or above) users who wish to make comments on news sites, please contact Jim Burton directly rather than using this list, and we can work on maximising view count.
Moral panic: Difference between revisions
The Admins (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
The Admins (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The concept is often used in the British sociological sense to refer to shorter-term events<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moral_panic Wikipedia - Moral Panic]</ref>, such as groups of hooligans or mods supposedly inciting flash panics in society, and the resulting authoritarian crackdowns. This (while it was the original usage, by Stanley Cohen), is a highly questionable phenomenon, since it usually relies on [[moral enterprise]] and media/institutional involvement to manufacture consent. Academics such as [[Bill Thompson]] describe the British theory of Moral Panic as a bourgeoise construct of middle-class sociologists who themselves partake in this manufacturing of consent and benefit from it. | The concept is often used in the British sociological sense to refer to shorter-term events<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moral_panic Wikipedia - Moral Panic]</ref>, such as groups of hooligans or mods supposedly inciting flash panics in society, and the resulting authoritarian crackdowns. This (while it was the original usage, by Stanley Cohen), is a highly questionable phenomenon, since it usually relies on [[moral enterprise]] and media/institutional involvement to manufacture consent. Academics such as [[Bill Thompson]] describe the British theory of Moral Panic as a bourgeoise construct of middle-class sociologists who themselves partake in this manufacturing of consent and benefit from it. | ||
==Timeline== | |||
*'''1950s''' - "The state conflated the category of the male homosexual with the category of the child molester; in the eyes of the state, all homosexuals were potential child molesters, and vice-versa. The notion of the “pedophile,” as distinct from the “homosexual,” was not prevalent. Police departments cracked down increasingly on men who were involved in sexual activity with teenage boys, some of whom were actually straight hustlers whom the state criminalized as “juvenile delinquents.”"<ref name=DeOrio>https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/handle/2027.42/138757/sadeorio_1.pdf De Orio</ref> | |||
*'''Late 1960s<ref>[https://slate.com/human-interest/2012/07/the-chickens-and-the-bulls-the-rise-and-incredible-fall-of-a-vicious-extortion-ring-that-preyed-on-prominent-gay-men-in-the-1960s.html Late 1960s - Slate.com]</ref>''' - for a long time, the mob had run extortion schemes against prominent pederasts and gays, however, the 60s were a time of relative latency in the war against sex offenders. Gay liberation and homophile activists were joined by sexual freedom activists, and progress began to be made with law reforms.<ref name=DeOrio/> | |||
*'''April 1971''' – Florence Rush presents her ground-breaking: “The Sexual Abuse of Children: A Feminist Point of View” about childhood sexual abuse and incest, at the New York Radical Feminists Rape Conference. Focus is on sexual violence against female children within the family, seen as a pervasive, if not universal factor in socializing females to accept subservient & submissive role in society. Sexual violence is reframed as an inherently political, women’s issue. | |||
*'''1973''' – Revelations that dozens of teenage boys had been tortured, raped, murdered and secretly buried by serial killer Dean Corll. Rumors that the boys had been involved in prostitution and/or pornography are encouraged by Police leadership, blaming victim “lifestyle” for the tragedy to offset parent’s revelations that police had refused to investigate the disappearance of the early victims. No verification of lifestyle claims from any family members or friends of the deceased. | |||
*Boy prostitution and pornography operations subsequently uncovered in California, the [[Lyric International|DOM-LYRIC]] case, and in Houston, the Roy Ames case, 1973-75, but no link to Corll. | |||
*'''1975''' – Dr [[Judianne Densen-Gerber]] publishes ''“Incest as a causative factor in anti-social behavior: An exploratory study”'' in Contemporary Drug Problems. Establishes incest of female children as a public health issue linked to drug addiction and prostitution. | |||
*Family members of children living in Christian Brothers run orphanage in Newfoundland Canada, supported by a concerned community employee, attempt to reveal the long history of physical and sexual abuse of the boys by the staff, which is ongoing. The whistle is blown over local radio, inciting police investigation but is quashed by collusion of prominent Catholics. Efforts continue however, over the next decade. | |||
*'''1974–76''' – Pederast network shut down by police investigation and successful prosecution of several principle conspirators, revealed in three linked cases: the New Orleans Boy Scout troop (Halvorsen), the Tennessee Boy’s Farm (Vermylie) and Brother Paul’s Christian Mission – Michigan (Gerald Richards). Dozens of boys aged 10-19 years linked with multiple men in prostitution and pornography operations over the previous 5 years. Perpetrators ran charities providing services to “wayward” or delinquent boys previously identified as juvenile prostitutes, including short and long term crisis housing. Images of the victims published as pornography. | |||
*'''1977''' - [[Anita Bryant]] launches her divisive [[Save Our Children]] campaign, splitting the gay movement against the pederasts. While some radical voices argued for age inclusivity, the dominant faction saw that as a recipe for disaster and (foreshadowing the gay marriage movement) tried to minimize the differences between gay culture and heteronormativity, assimilating itself first to the latter's stigmatization of youth sexuality as deviant and harmful and later to its stigmatization of all sex outside of marriage (or, at least, of a monogamous relationship). "Consenting Adults" became the slogan for gay assimilationism.<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Save_Our_Children Save Our Children]</ref><ref>[https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/handle/2027.42/138757/sadeorio_1.pdf Scott De Orio]</ref> | |||
*'''1977–79''' – Densen-Gerber and Det. Lloyd Martin (LAPD) aggressively lobby state and federal legislators for new laws effectively banning and criminalizing possession or sale of [[child pornography]]. Heavy print media coverage of these issues, multiple hearings with testimony from various social sciences experts, incarcerated perpetrators, models. Victimization of children in state or private custody of various kinds is a secondary focus. | |||
*'''1978''' – John Wayne Gacy confessed to police that since 1972, he had sexually assaulted, tortured and murdered approximately 25 to 30 teenage male, whom he falsely claimed were all runaways or male prostitutes, burying many of them in a crawlspace under his home. | |||
*'''1979''' – Jonathan Gathorne-Hardy publishes “The Public School Phenomenon” in the UK, documenting a long history & culture of relationships between older and younger students, as well as violence perpetrated on residents by other residents and staff. | |||
*'''1980''' – [[Lawrence Pazder]] publishes [[Michelle Remembers]], inventing the terminology and concepts of [[Satanic Ritual Abuse]]/Ritual Abuse/Ritualized Abuse. Pazder attempts to have Michelle Smith declared a living saint by the Vatican. | |||
*'''1982-86''' - Johnny Gosch<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disappearance_of_Johnny_Gosch Wikipedia: Johnny Gosch]</ref> and a succession of other Des Moines teenage boys go missing over the following years. Speculation is rife as to organized pedophile conspiracy. | |||
*'''1983''' – the first adult women claiming to be survivors of SRA are being evaluated and studied by psychiatric staff in California. Allegations are of long term sadistic abuse by satanic family cult members, with supernatural elements and frequent diagnosis of the previously rare Multiple Personality Disorder. | |||
*'''1985''' – media coverage of CSA issues is entirely focused on women’s allegations of satanic cult abuse and mind control in childhood, or large-scale daycare abuse accusation cases with allegations by some parents that children have revealed SRA victimization. Child protection resources are also dominated by cases of this nature, as are police child sex crime investigation resources, and psychiatric treatment/ therapy services for women and child sexual abuse victims. This social situation persists throughout the decade. | |||
==Quotes on moral panic== | ==Quotes on moral panic== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 43: | ||
:''"One of the things we want to make sure that we don’t do is something that feels good or looks good or causes the public to relax."''[http://www.king5.com/topstories/stories/NW_011409WAB-surgically-implanted-gps-TP.28c9413.html] | :''"One of the things we want to make sure that we don’t do is something that feels good or looks good or causes the public to relax."''[http://www.king5.com/topstories/stories/NW_011409WAB-surgically-implanted-gps-TP.28c9413.html] | ||
==References== | |||
Revision as of 19:30, 1 January 2022
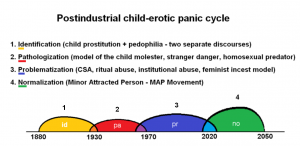
Moral panic refers to a phenomenon in which mainstream society experiences large amounts of fear and uncertainty fuelled by the perception that a particular moral institution (such as childhood innocence) or group of people (such as children) is under threat. The perceived threat often comes in the form of a socially excluded, alien group of people (pedophiles or sex offenders) and the ideologies and real life events attributed to them. Necessary to the incitement of moral panic is the persistant exchange of misinformation, by the media for example.
The concept is often used in the British sociological sense to refer to shorter-term events[1], such as groups of hooligans or mods supposedly inciting flash panics in society, and the resulting authoritarian crackdowns. This (while it was the original usage, by Stanley Cohen), is a highly questionable phenomenon, since it usually relies on moral enterprise and media/institutional involvement to manufacture consent. Academics such as Bill Thompson describe the British theory of Moral Panic as a bourgeoise construct of middle-class sociologists who themselves partake in this manufacturing of consent and benefit from it.
Timeline
- 1950s - "The state conflated the category of the male homosexual with the category of the child molester; in the eyes of the state, all homosexuals were potential child molesters, and vice-versa. The notion of the “pedophile,” as distinct from the “homosexual,” was not prevalent. Police departments cracked down increasingly on men who were involved in sexual activity with teenage boys, some of whom were actually straight hustlers whom the state criminalized as “juvenile delinquents.”"[2]
- Late 1960s[3] - for a long time, the mob had run extortion schemes against prominent pederasts and gays, however, the 60s were a time of relative latency in the war against sex offenders. Gay liberation and homophile activists were joined by sexual freedom activists, and progress began to be made with law reforms.[2]
- April 1971 – Florence Rush presents her ground-breaking: “The Sexual Abuse of Children: A Feminist Point of View” about childhood sexual abuse and incest, at the New York Radical Feminists Rape Conference. Focus is on sexual violence against female children within the family, seen as a pervasive, if not universal factor in socializing females to accept subservient & submissive role in society. Sexual violence is reframed as an inherently political, women’s issue.
- 1973 – Revelations that dozens of teenage boys had been tortured, raped, murdered and secretly buried by serial killer Dean Corll. Rumors that the boys had been involved in prostitution and/or pornography are encouraged by Police leadership, blaming victim “lifestyle” for the tragedy to offset parent’s revelations that police had refused to investigate the disappearance of the early victims. No verification of lifestyle claims from any family members or friends of the deceased.
- Boy prostitution and pornography operations subsequently uncovered in California, the DOM-LYRIC case, and in Houston, the Roy Ames case, 1973-75, but no link to Corll.
- 1975 – Dr Judianne Densen-Gerber publishes “Incest as a causative factor in anti-social behavior: An exploratory study” in Contemporary Drug Problems. Establishes incest of female children as a public health issue linked to drug addiction and prostitution.
- Family members of children living in Christian Brothers run orphanage in Newfoundland Canada, supported by a concerned community employee, attempt to reveal the long history of physical and sexual abuse of the boys by the staff, which is ongoing. The whistle is blown over local radio, inciting police investigation but is quashed by collusion of prominent Catholics. Efforts continue however, over the next decade.
- 1974–76 – Pederast network shut down by police investigation and successful prosecution of several principle conspirators, revealed in three linked cases: the New Orleans Boy Scout troop (Halvorsen), the Tennessee Boy’s Farm (Vermylie) and Brother Paul’s Christian Mission – Michigan (Gerald Richards). Dozens of boys aged 10-19 years linked with multiple men in prostitution and pornography operations over the previous 5 years. Perpetrators ran charities providing services to “wayward” or delinquent boys previously identified as juvenile prostitutes, including short and long term crisis housing. Images of the victims published as pornography.
- 1977 - Anita Bryant launches her divisive Save Our Children campaign, splitting the gay movement against the pederasts. While some radical voices argued for age inclusivity, the dominant faction saw that as a recipe for disaster and (foreshadowing the gay marriage movement) tried to minimize the differences between gay culture and heteronormativity, assimilating itself first to the latter's stigmatization of youth sexuality as deviant and harmful and later to its stigmatization of all sex outside of marriage (or, at least, of a monogamous relationship). "Consenting Adults" became the slogan for gay assimilationism.[4][5]
- 1977–79 – Densen-Gerber and Det. Lloyd Martin (LAPD) aggressively lobby state and federal legislators for new laws effectively banning and criminalizing possession or sale of child pornography. Heavy print media coverage of these issues, multiple hearings with testimony from various social sciences experts, incarcerated perpetrators, models. Victimization of children in state or private custody of various kinds is a secondary focus.
- 1978 – John Wayne Gacy confessed to police that since 1972, he had sexually assaulted, tortured and murdered approximately 25 to 30 teenage male, whom he falsely claimed were all runaways or male prostitutes, burying many of them in a crawlspace under his home.
- 1979 – Jonathan Gathorne-Hardy publishes “The Public School Phenomenon” in the UK, documenting a long history & culture of relationships between older and younger students, as well as violence perpetrated on residents by other residents and staff.
- 1980 – Lawrence Pazder publishes Michelle Remembers, inventing the terminology and concepts of Satanic Ritual Abuse/Ritual Abuse/Ritualized Abuse. Pazder attempts to have Michelle Smith declared a living saint by the Vatican.
- 1982-86 - Johnny Gosch[6] and a succession of other Des Moines teenage boys go missing over the following years. Speculation is rife as to organized pedophile conspiracy.
- 1983 – the first adult women claiming to be survivors of SRA are being evaluated and studied by psychiatric staff in California. Allegations are of long term sadistic abuse by satanic family cult members, with supernatural elements and frequent diagnosis of the previously rare Multiple Personality Disorder.
- 1985 – media coverage of CSA issues is entirely focused on women’s allegations of satanic cult abuse and mind control in childhood, or large-scale daycare abuse accusation cases with allegations by some parents that children have revealed SRA victimization. Child protection resources are also dominated by cases of this nature, as are police child sex crime investigation resources, and psychiatric treatment/ therapy services for women and child sexual abuse victims. This social situation persists throughout the decade.
Quotes on moral panic
Don Pierce, a Sex offender GPS tracking expert on the possibility of surgically implanted GPS for sex offenders:
- "One of the things we want to make sure that we don’t do is something that feels good or looks good or causes the public to relax."[1]