Research: Who offends and how often?: Difference between revisions
The Admins (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{research}}__NOTOC__ | {{research}}__NOTOC__ | ||
Professional and public discourse on ''who offends and how often,'' with respect to minors, is confused by conflicting mythology that has evolved over time, if only for reasons of expedience. | |||
Private organizations marketing child protection products, training and software towards parents claim that [[Debate Guide: "Stranger danger" or "It could be anyone"|"strangers" are the number one concern]] when it comes to protecting children. Government statistics, academia, human rights and sex offender rights groups paint a different picture. | |||
This disagreement has been capitalized upon by political opportunists who use the new data to support the newer myth that [[Debate Guide: "Stranger danger" or "It could be anyone"|''everybody'' is a considerable threat]] to children. | |||
==Who offends?== | ==Who offends?== | ||
The statistics do appear to indicate that most child abuse in general is perpetrated by parents. In fact, if exposure times are to be taken into consideration, it may even be the case that parents have an abnormal ''tendency'' to abuse or have sex with their children. | The statistics do appear to indicate that most child abuse in general is perpetrated by parents. In fact, if exposure times are to be taken into consideration, it may even be the case that parents have an abnormal ''tendency'' to abuse or have sex with their children. As for sexual offenses (when defined as all, rather than reported offending), '''between 70 and 80% of perpetrators are other minors'''.<ref>[https://sci-hub.se/https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1077559519873975 Finkelhor - Sexual Abuse and Assault in a Large National Sample of Children and Adolescents]</ref> Even when prosecution was involved, official statistics appear to reveal that minors are prosecuted frequently, even for [[child pornography]]: | ||
*In Canada, the majority of incidents involving non-consensual sharing of images involve a minor perpetrator.<ref>[https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/85-002-x/2022001/article/00008-eng.htm Non-consensual distribution of intimate images, an offence predominantly involving youth aged 12 to 17 Online child sexual exploitation and abuse in Canada: A statistical profile of police-reported incidents and court charges, 2014 to 2020]</ref> | |||
*In the Netherlands, 1 in 12 Child Pornography prosecutions involves a minor perpetrator.<ref>[https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263382630_Child_pornography_the_Internet_and_juvenile_suspects Leukfeldt, E. R., Jansen, J., & Stol, W. P. (2013). Child pornography, the Internet and juvenile suspects. Journal of Social Welfare and Family Law, 36(1), 3–13. doi:10.1080/09649069.2013.851178]</ref> | |||
*In the US, in 2010, 23% of Child Pornography offenders were under 21.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20120916071520/https://www.ussc.gov/Data_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2010/Table06.pdf USSC.gov: Sourcebook]</ref> | |||
*In the US in 2009, 23% of people prosecuted for Child Pornography production were minors, half of which were entirely consensual and did not involve blackmail.<ref>[https://scholars.unh.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1046&context=ccrc Trends in Arrests for Child Pornography Production: The Third National Juvenile Online Victimization Study (NJOV‐3)National Juvenile Online Victimization Study (NJOV 3]</ref> | |||
[[Image:Usdojap.PNG|thumb|left|From Snyder (2000): The peak "perpetrator" activity is at 14-16 (click to expand)]]Conviction-wise, 14-16 are the peak ages for sexual activity with American minors, and it does appear that sexual assault laws are used to prosecute "children" in a significant minority of all cases involving a minor "victim". | [[Image:Usdojap.PNG|thumb|left|From Snyder (2000): The peak "perpetrator" activity is at 14-16 (click to expand)]]Conviction-wise, 14-16 are the peak ages for sexual activity with American minors, and it does appear that sexual assault laws are used to prosecute "children" in a significant minority of all cases involving a minor "victim". | ||
| Line 13: | Line 22: | ||
*'''Howard N. Snyder, Ph.D (2000). [http://web.archive.org/web/20090726145557/http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov//bjs///pub/pdf/saycrle.pdf Sexual Assault of Young Children as Reported to Law Enforcement: Victim, Incident, and Offender Characteristics], USDOJ/National Center for Juvenile Justice.''' | *'''Howard N. Snyder, Ph.D (2000). [http://web.archive.org/web/20090726145557/http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov//bjs///pub/pdf/saycrle.pdf Sexual Assault of Young Children as Reported to Law Enforcement: Victim, Incident, and Offender Characteristics], USDOJ/National Center for Juvenile Justice.''' | ||
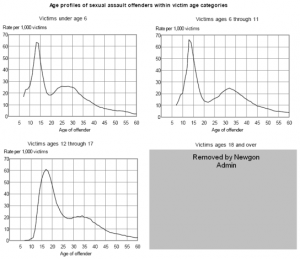
*:"Nearly all of the offenders in sexual assaults reported to law enforcement were male (96%). Female offenders were most common in assaults against victims under age 6. For these youngest victims, 12% of offenders were females, compared with 6% for victims ages 6 through 12, and 3% for victims ages 12 through 17. Overall, 6% of the offenders who sexually assaulted juveniles were female, compared with just 1% of the female offenders who sexually assaulted adults. (...) The age profile of offenders varied with the age of the victim (figure 7). Juvenile offenders assaulted 4% of adult victims, while adult offenders assaulted 67% of juvenile victims." | *:"Nearly all of the offenders in sexual assaults reported to law enforcement were male (96%). Female offenders were most common in assaults against victims under age 6. For these youngest victims, 12% of offenders were females, compared with 6% for victims ages 6 through 12, and 3% for victims ages 12 through 17. Overall, 6% of the offenders who sexually assaulted juveniles were female, compared with just 1% of the female offenders who sexually assaulted adults. (...) The age profile of offenders varied with the age of the victim (figure 7). Juvenile offenders assaulted 4% of adult victims, while adult offenders assaulted 67% of juvenile victims." | ||
*'''Sophie King-Hill et al. (2023). [https://books.google.lu/books?hl=ru&lr=&id=s33GEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR5&dq=info:DibugGiaObkJ:scholar.google.com/&ots=_EDy1uumb1&sig=NGD8cW5DFjrnd90212ffSKRvGgQ&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false ''Understanding and Responding to Sibling Sexual Abuse''] (Palgrave Macmillan)''' | |||
*:"[B]etween one-fifth to one-third of all CSA is carried out by another child (Hackett 2014) and that a significant proportion of this child-on-child sexual abuse is intrafamilial (Yates and Allardyce 2021). | |||
*:[...] [A]dults who have been sexually abused by a sibling in childhood may only categorise it as abusive in retrospect (Hardy 2001). As seen in Hardy's (2001) research: | |||
*:<blockquote>''The number of respondents who believed their sibling interactions to have been [sexually] abusive increased dramatically from the time it occurred to the present, rising from 6.6% to 33.3%. (p.11)[...]''</blockquote> | |||
*:[I]n the United Kingdom (UK), it is estimated that approximately one-third to one-fifth of CSA is exhibited by another child/young person (Hackett 2004, 2014). [... T]he Radford et al. (2011) Report on child abuse and neglect in the UK found that 65.9% of contact sexual abuse reported by children aged (0-17 years) was committed by another child under the age of 18 years. | |||
*:Estimates of the prevalence of sibling sexual behaviour within the general population range from 2% (Russell 1986) to 4.7% (Griffce ct al. 2014), 6.5% (Atwood 2007), 7.4% (Hardy 2001) and l3% (Finkelhor 1980)." | |||
*'''McPhail, I.V. (2024) “[https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11930-023-00381-y The Subjective Experience of Individuals with Pedohebephilic Interest]”, ''Current Sexual Health Reports'' 16, DOI: 10.1007/s11930-023-00381-y''' | |||
*:from the [https://www.b4uact.org/b4qr/vol4/spring2024/ B4QR] description of the article: | |||
*:“McPhail examines the prevalence of MAPs who engage in sexual behaviors with children, citing studies showing that in individuals convicted of sex crimes against children, attraction to children predicts future offending. Further, he indicates that those who are exclusively or preferentially attracted to children have higher risks of engaging in sexual behavior involving children after receiving legal sanctions. While not explicitly noted by McPhail, these studies focus on forensic populations. This clarification would help the reader understand the context of the sample population and prevent the incorrect generalizability of findings to the MAP population at large. Additionally, in various studies, a significant percentage of MAPs self-report engaging in sexual behavior with children (13-90%) or accessing sexual images of minors (10-64%). Despite stark variations in reported percentages, McPhail does not explicitly address this wide range.” | |||
===Juvenile offending: The fallacy of "Special Treatment"=== | ===Juvenile offending: The fallacy of "Special Treatment"=== | ||
Some liberals, academics and advocates for [[Sex offender registry|SOR]] reform have argued that juvenile sexual offenders against minors are a "special case", requiring "special treatment" ''because'' they offend on a less frequent basis and are easier to "cure". Whilst the former is demonstrably false, it should also be noted that juvenile sexual offenders against minors are [[Research: Recidivism and other offending figures|''significantly more likely to re-offend'']] than their adult peers (when counting all crimes). This is a general trend of high reoffending throughout most of the youth offender population regardless of the nature of the initial offense, sexual or otherwise. This trend contradicts the common narrative of [[Research: Cognitive ability|teenagers as uniquely malleable]], or in need of any "second chance" | Some liberals, academics and advocates for [[Sex offender registry|SOR]] reform have argued that juvenile sexual offenders against minors are a "special case", requiring "special treatment" ''because'' they offend on a less frequent basis and are easier to "cure". Whilst the former is demonstrably false, it should also be noted that juvenile sexual offenders against minors are [[Research: Recidivism and other offending figures|''significantly more likely to re-offend'']] than their adult peers (when counting all crimes). This is a general trend of high reoffending throughout most of the youth offender population regardless of the nature of the initial offense, sexual or otherwise.<ref>[https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/199224/compendium-of-reoffending-statistics-and-analysis.pdf UK MoJ - Compendium of reoffending statistics and analysis] ''"Juveniles receiving a reprimand or warning between 2000 and 2008 have a higher proven reoffending rate than adult offenders receiving a caution. In 2008, 25.5 per cent of juveniles receiving a reprimand or warning and 19.2 percent of adults receiving a caution reoffended within one year. An offender enters the Criminal Justice System on the day they received their first reprimand, warning, caution or conviction. In 2008, 21 per cent of juveniles and 9 per cent of adults entering the Criminal Justice System reoffended within a year"'' (Editor note: while the overall reoffending rates displayed in this document are almost identical, this is because the juvenile rates include cautions in their sampling, therefore including less serious crime for juveniles).</ref><ref>[https://www.aic.gov.au/publications/tandi/tandi284 Aus Govt: Current trends in the rehabilitation of juvenile offenders]</ref><ref>[https://info.mstservices.com/blog/juvenile-recidivism-rates Do We Know The Full Extent of Juvenile Recidivism?]</ref><ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9186365/ Child pornography possession/receipt offenders: developing a forensic profile (see "Arrest Onset")]</ref> This trend contradicts the common narrative of [[Research: Cognitive ability|teenagers as uniquely malleable]], or in need of any "second chance" privileges not afforded to adults. | ||
==How often?== | ==How often?== | ||
The actual prevalence of abusive sexual | The actual prevalence of abusive sexual behaviors with children has been exaggerated by over broad definitions. | ||
*'''Haugaard, J.J. (2000). "The challenge of defining child sexual abuse," ''American Psychologist'', 55(9), 1036-1039.''' | *'''Haugaard, J.J. (2000). "The challenge of defining child sexual abuse," ''American Psychologist'', 55(9), 1036-1039.''' | ||
| Line 26: | Line 46: | ||
*'''World Health Organization (1986). "[https://books.google.com/books/about/Child_Sexual_Abuse.html?id=kH-WOAAACAAJ Child sexual abuse: report on a consultation, Copenhagen, 11-12 December 1985]."''' | *'''World Health Organization (1986). "[https://books.google.com/books/about/Child_Sexual_Abuse.html?id=kH-WOAAACAAJ Child sexual abuse: report on a consultation, Copenhagen, 11-12 December 1985]."''' | ||
*:"In all studies most of the cases are single incidents of indecent exposure, propositions to do something sexual which are rejected by the child, and brief genital touching. Offenses involving some degree of force or prolonged or repeated abuse by the same person have been experienced by about one percent of the populations studied." | *:"In all studies most of the cases are single incidents of indecent exposure, propositions to do something sexual which are rejected by the child, and brief genital touching. Offenses involving some degree of force or prolonged or repeated abuse by the same person have been experienced by about one percent of the populations studied." | ||
* '''Dombert et al. (2016) [https://www.wellesu.com/10.1080/00224499.2015.1020108 How Common is Men's Self-Reported Sexual Interest in Prepubescent Children?] ''J Sex Res.''; 53(2):214-23. doi: 10.1080/00224499.2015.1020108''' | |||
*: "In an online survey of 8,718 German men, 4.1% reported sexual fantasies involving prepubescent children, 3.2% reported sexual offending against prepubescent children, and 0.1% reported a pedophilic sexual preference. [...] Of all participants, 5.5% (n = 482) reported any indication of pedophilic sexual interest (i.e., any report of fantasy, behavior, child pornography consumption, having paid a child for sexual services, or traveling to another country with intent to have sexual contact with a child). Specifically, 4.1% (n = 358) reported sexual fantasies involving prepubescent children (Table 1). The majority of men who fantasized about children reported fantasies about girls (68.4%; n = 245), 13.1% (n = 47) about boys, and 18.4% (n = 66) about boys and girls. Overall, 3.2% (n = 280) of the participants indicated sexual behavior involving prepubescent children, with 1.7% (n = 148) indicating child pornography use exclusively, 0.8% (n = 71) reporting sexual contact with children, and 0.7% (n = 61) affirming both offense categories" | |||
===Abduction=== | ===Abduction=== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 59: | ||
:*Most "abductions" turned out to involve family members. | :*Most "abductions" turned out to involve family members. | ||
:*Only 115 of all the cases reported involved abduction by a stranger. | :*Only 115 of all the cases reported involved abduction by a stranger. | ||
==References== | |||
[[Category:Official Encyclopedia]][[Category:Research: Victimology and other Pseudoscience]][[Category:Research into effects on Children]] | [[Category:Official Encyclopedia]][[Category:Research: Victimology and other Pseudoscience]][[Category:Research into effects on Children]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:11, 9 November 2024
 | ||||||||||||
| Part of NewgonWiki's research project | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| Template: Research - This template |
Professional and public discourse on who offends and how often, with respect to minors, is confused by conflicting mythology that has evolved over time, if only for reasons of expedience.
Private organizations marketing child protection products, training and software towards parents claim that "strangers" are the number one concern when it comes to protecting children. Government statistics, academia, human rights and sex offender rights groups paint a different picture.
This disagreement has been capitalized upon by political opportunists who use the new data to support the newer myth that everybody is a considerable threat to children.
Who offends?
The statistics do appear to indicate that most child abuse in general is perpetrated by parents. In fact, if exposure times are to be taken into consideration, it may even be the case that parents have an abnormal tendency to abuse or have sex with their children. As for sexual offenses (when defined as all, rather than reported offending), between 70 and 80% of perpetrators are other minors.[1] Even when prosecution was involved, official statistics appear to reveal that minors are prosecuted frequently, even for child pornography:
- In Canada, the majority of incidents involving non-consensual sharing of images involve a minor perpetrator.[2]
- In the Netherlands, 1 in 12 Child Pornography prosecutions involves a minor perpetrator.[3]
- In the US, in 2010, 23% of Child Pornography offenders were under 21.[4]
- In the US in 2009, 23% of people prosecuted for Child Pornography production were minors, half of which were entirely consensual and did not involve blackmail.[5]
Conviction-wise, 14-16 are the peak ages for sexual activity with American minors, and it does appear that sexual assault laws are used to prosecute "children" in a significant minority of all cases involving a minor "victim".
- US Department of Health and Human Services (2006). Child Maltreatment 2006, chapter 3, Victims by Perpetrator Relationship.
- 82% of child maltreatment (or more) involved a parent. 17% was known to involve a non-parent.
- Howard N. Snyder, Ph.D (2000). Sexual Assault of Young Children as Reported to Law Enforcement: Victim, Incident, and Offender Characteristics, USDOJ/National Center for Juvenile Justice.
- "Nearly all of the offenders in sexual assaults reported to law enforcement were male (96%). Female offenders were most common in assaults against victims under age 6. For these youngest victims, 12% of offenders were females, compared with 6% for victims ages 6 through 12, and 3% for victims ages 12 through 17. Overall, 6% of the offenders who sexually assaulted juveniles were female, compared with just 1% of the female offenders who sexually assaulted adults. (...) The age profile of offenders varied with the age of the victim (figure 7). Juvenile offenders assaulted 4% of adult victims, while adult offenders assaulted 67% of juvenile victims."
- Sophie King-Hill et al. (2023). Understanding and Responding to Sibling Sexual Abuse (Palgrave Macmillan)
- "[B]etween one-fifth to one-third of all CSA is carried out by another child (Hackett 2014) and that a significant proportion of this child-on-child sexual abuse is intrafamilial (Yates and Allardyce 2021).
- [...] [A]dults who have been sexually abused by a sibling in childhood may only categorise it as abusive in retrospect (Hardy 2001). As seen in Hardy's (2001) research:
The number of respondents who believed their sibling interactions to have been [sexually] abusive increased dramatically from the time it occurred to the present, rising from 6.6% to 33.3%. (p.11)[...]
- [I]n the United Kingdom (UK), it is estimated that approximately one-third to one-fifth of CSA is exhibited by another child/young person (Hackett 2004, 2014). [... T]he Radford et al. (2011) Report on child abuse and neglect in the UK found that 65.9% of contact sexual abuse reported by children aged (0-17 years) was committed by another child under the age of 18 years.
- Estimates of the prevalence of sibling sexual behaviour within the general population range from 2% (Russell 1986) to 4.7% (Griffce ct al. 2014), 6.5% (Atwood 2007), 7.4% (Hardy 2001) and l3% (Finkelhor 1980)."
- McPhail, I.V. (2024) “The Subjective Experience of Individuals with Pedohebephilic Interest”, Current Sexual Health Reports 16, DOI: 10.1007/s11930-023-00381-y
- from the B4QR description of the article:
- “McPhail examines the prevalence of MAPs who engage in sexual behaviors with children, citing studies showing that in individuals convicted of sex crimes against children, attraction to children predicts future offending. Further, he indicates that those who are exclusively or preferentially attracted to children have higher risks of engaging in sexual behavior involving children after receiving legal sanctions. While not explicitly noted by McPhail, these studies focus on forensic populations. This clarification would help the reader understand the context of the sample population and prevent the incorrect generalizability of findings to the MAP population at large. Additionally, in various studies, a significant percentage of MAPs self-report engaging in sexual behavior with children (13-90%) or accessing sexual images of minors (10-64%). Despite stark variations in reported percentages, McPhail does not explicitly address this wide range.”
Juvenile offending: The fallacy of "Special Treatment"
Some liberals, academics and advocates for SOR reform have argued that juvenile sexual offenders against minors are a "special case", requiring "special treatment" because they offend on a less frequent basis and are easier to "cure". Whilst the former is demonstrably false, it should also be noted that juvenile sexual offenders against minors are significantly more likely to re-offend than their adult peers (when counting all crimes). This is a general trend of high reoffending throughout most of the youth offender population regardless of the nature of the initial offense, sexual or otherwise.[6][7][8][9] This trend contradicts the common narrative of teenagers as uniquely malleable, or in need of any "second chance" privileges not afforded to adults.
How often?
The actual prevalence of abusive sexual behaviors with children has been exaggerated by over broad definitions.
- Haugaard, J.J. (2000). "The challenge of defining child sexual abuse," American Psychologist, 55(9), 1036-1039.
- "For example, some researchers have considered children to be those below the age of 18 (Russell, 1983; Wyatt, 1985), those below the age of 17 (Finkelhor, 1979; Fromuth, 1986), or those below the age of 16 (Wurr & Partridge, 1996). In addition, defining the term sexual behavior has been difficult. Although some behaviors are considered sexual by almost everyone (e.g., intercourse, genital fondling), there is less agreement about other behaviors, such as bathing children or sleeping with them. Finally, controversy also exists about the meaning of the word abuse. Some have argued that abuse, as used in scientific research, indicates the presence of harm (Rind, Tromovitch, & Bauserman, 1998) and that, consequently, child sexual abuse may not be an appropriate term to describe adult–child sexual encounters from which no demonstrable harm can be observed. [...] First, studies have reported higher prevalence rates with broad definitions than they would have with more restricted definitions. For example, some studies with community samples have reported that as many as 50%–60% of girls are sexually abused by an adult before the age of 18 (Russell, 1983; Wyatt, 1985). These high rates raised public concern about child sexual abuse, and this increased concern may have resulted in many abused children and their families receiving services that might not have been available otherwise."
- World Health Organization (1986). "Child sexual abuse: report on a consultation, Copenhagen, 11-12 December 1985."
- "In all studies most of the cases are single incidents of indecent exposure, propositions to do something sexual which are rejected by the child, and brief genital touching. Offenses involving some degree of force or prolonged or repeated abuse by the same person have been experienced by about one percent of the populations studied."
- Dombert et al. (2016) How Common is Men's Self-Reported Sexual Interest in Prepubescent Children? J Sex Res.; 53(2):214-23. doi: 10.1080/00224499.2015.1020108
- "In an online survey of 8,718 German men, 4.1% reported sexual fantasies involving prepubescent children, 3.2% reported sexual offending against prepubescent children, and 0.1% reported a pedophilic sexual preference. [...] Of all participants, 5.5% (n = 482) reported any indication of pedophilic sexual interest (i.e., any report of fantasy, behavior, child pornography consumption, having paid a child for sexual services, or traveling to another country with intent to have sexual contact with a child). Specifically, 4.1% (n = 358) reported sexual fantasies involving prepubescent children (Table 1). The majority of men who fantasized about children reported fantasies about girls (68.4%; n = 245), 13.1% (n = 47) about boys, and 18.4% (n = 66) about boys and girls. Overall, 3.2% (n = 280) of the participants indicated sexual behavior involving prepubescent children, with 1.7% (n = 148) indicating child pornography use exclusively, 0.8% (n = 71) reporting sexual contact with children, and 0.7% (n = 61) affirming both offense categories"
Abduction
Stereotypical child abductions by strangers are incredibly rare, even in countries where mass media have incited the most fear. Again, broad definitions of "missing" have contributed to a hyping of fears regarding abduction.
- Andrea J. Sedlak, David Finkelhor, Heather Hammer, and Dana J. Schultz. U.S. Department of Justice. "National Estimates of Missing Children: An Overview" in National Incidence Studies of Missing, Abducted, Runaway, and Thrownaway Children. Washington, DC: Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice, October 2002.
- Of the 800,000 children who were reported missing that year, half turned out to be runaways.
- Most "abductions" turned out to involve family members.
- Only 115 of all the cases reported involved abduction by a stranger.
References
- ↑ Finkelhor - Sexual Abuse and Assault in a Large National Sample of Children and Adolescents
- ↑ Non-consensual distribution of intimate images, an offence predominantly involving youth aged 12 to 17 Online child sexual exploitation and abuse in Canada: A statistical profile of police-reported incidents and court charges, 2014 to 2020
- ↑ Leukfeldt, E. R., Jansen, J., & Stol, W. P. (2013). Child pornography, the Internet and juvenile suspects. Journal of Social Welfare and Family Law, 36(1), 3–13. doi:10.1080/09649069.2013.851178
- ↑ USSC.gov: Sourcebook
- ↑ Trends in Arrests for Child Pornography Production: The Third National Juvenile Online Victimization Study (NJOV‐3)National Juvenile Online Victimization Study (NJOV 3
- ↑ UK MoJ - Compendium of reoffending statistics and analysis "Juveniles receiving a reprimand or warning between 2000 and 2008 have a higher proven reoffending rate than adult offenders receiving a caution. In 2008, 25.5 per cent of juveniles receiving a reprimand or warning and 19.2 percent of adults receiving a caution reoffended within one year. An offender enters the Criminal Justice System on the day they received their first reprimand, warning, caution or conviction. In 2008, 21 per cent of juveniles and 9 per cent of adults entering the Criminal Justice System reoffended within a year" (Editor note: while the overall reoffending rates displayed in this document are almost identical, this is because the juvenile rates include cautions in their sampling, therefore including less serious crime for juveniles).
- ↑ Aus Govt: Current trends in the rehabilitation of juvenile offenders
- ↑ Do We Know The Full Extent of Juvenile Recidivism?
- ↑ Child pornography possession/receipt offenders: developing a forensic profile (see "Arrest Onset")