One of our staff members is contributing considerably to a News Archiving service at Mu. Any well educated (Masters, PhD or above) users who wish to make comments on news sites, please contact Jim Burton directly rather than using this list, and we can work on maximising view count.
Debate Guide: Cognitive ability = consent: Difference between revisions
The Admins (talk | contribs) |
The Admins (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Ageism (social justice argument)== | ==Ageism (social justice argument)== | ||
If you are to apply an extreme social justice model, it is also [[Ageism|ageist]] to describe the cognitive abilities of prepubescent children as inferior, even if scores on problem solving tasks are lower. | If you are to apply an extreme social justice model, it is also [[Ageism|ageist]] to describe the cognitive abilities of prepubescent children as inferior, even if scores on problem solving tasks are lower. Social Justice approaches take into account ethnological differences between people and cultures, positing ways of conceptualizing those differences that do not focus on ''inferiority'', emphasizing how the socially dominant group [[Debate Guide: Social constructionism|constructs]] differences, loading them with meaning. Young people's abilities could perhaps be seen within a social-justice-informed [[Research: Evolutionary Perspectives on Intergenerational Sexuality|evolutionary biology]] framework, as ''best adapted'' to their age, needs and level of knowledge. IQ tests were invented by western adults and ten to classify the learnings and innate abilities of successful white western elders as superior, while neglecting other virtues. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 00:10, 8 December 2024
Children/Minors have not yet reached an adequate level of cognitive development to engage in sexual activity. They cannot consent because of this.
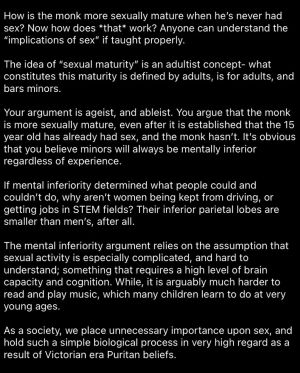
1. The underlying assertion about cognitive ability in all minors is problematic per se, as it seems that the human brain is adapted to its full evolutionary potential in early puberty.
2. The arbitrary concept of "informed consent" is highly problematic for ethical discussions about policies, as insisting on it renders CSA empirically invalid as a concept. If you want to quickly close down the debate on the basis of this dilemma - simply follow the CSA dilemma argument template.
Not compatible with sex-positive society
This argument relies on the assumption that sexual intimacy is especially complicated and hard to master; something requiring a higher level of cognition. Consider:
- Why do we freely physically abuse children "for their own good"?
- Why do families cart children and even teens off to "their" church for indoctrination as opposed to their neighbor's?
- Why do Americans then claim children are able to shoot a gun, and adults with Down syndrome or other mental impairments can consent to sex?
Are children having their consent to physical abuse, or religious indoctrination respected, given they are "unable" to?
Are the mentally impaired or senile giving their free, informed consent when they have sex or vote in an election?
Why (if informed consent is so important) is it now almost a cliche for women in western society to joke about getting drunk enough to have sex, and not even being able to recall their experiences?
The answer is that western society is slowly becoming more "sex positive". And in a "sex-positive" society, if we argue that minors' are not adequately developed to agree to sex, we must then also claim they do not have the cognitive ability to refuse it, a violation that can not be allowed.
A better approach would be to continue the deprogramming of sexual taboos at the same time as opposing the infantilization/oppression of young people and children.
This is something the nativist argument fails to identify or consider.
Ableism (egalitarian argument)
Using this argument's logic, one would be forced to question why some geriatrics, people with low IQs and the mentally ill/disabled should not be barred from experiencing sexual pleasure. Indeed, extending the cognitive argument yet further, Age of Consent laws would themselves be called into question, as the education system, IQ, social/emotional intelligence tests, would provide us with a better arbiter of "consenting ability" than an arbitrary cut-off age.
Ageism (social justice argument)
If you are to apply an extreme social justice model, it is also ageist to describe the cognitive abilities of prepubescent children as inferior, even if scores on problem solving tasks are lower. Social Justice approaches take into account ethnological differences between people and cultures, positing ways of conceptualizing those differences that do not focus on inferiority, emphasizing how the socially dominant group constructs differences, loading them with meaning. Young people's abilities could perhaps be seen within a social-justice-informed evolutionary biology framework, as best adapted to their age, needs and level of knowledge. IQ tests were invented by western adults and ten to classify the learnings and innate abilities of successful white western elders as superior, while neglecting other virtues.
See also
- Against: Power disparity - A similar argument, based on differences within a relationship.
Excerpt Graphic Library
While our research sections contain more information on the ethical issues described here, these may help in character-limited debates.
-
Bruce Rind on CSA concept (in)validity
-
Rind on lack of predictive validity for informed consent/CSA concept invalidity
-
Rind - CSA concept invalidity continued
-
David Finkelhor (Abuse Guru) and his failed moral circular argument
-
Robert Ehman on the failed circular "consent" argument
-
Robert Ehman on the real reasons for consent vs no consent binarism
-
Terry Leahy: Absence of an ethical argument against age-gap sex
-
Paul Okami on Power Imbalance argument (from Peer Commentaries on Green (2002) and Schmidt (2002))
-
Review of Sandfort and consent
-
Scott De Orio on Queer Identities that don't fit the model of consent
-
Liz Highleyman's review of Judith Levine's Harmful to Minors
-
Liz Highleyman's review of Judith Levine's Harmful to Minors: Consent dogma
-
Foucault, 1978
-
Steven Angelides on Power Imbalance argument from Feminism, Child Sexual Abuse, and the Erasure of Child Sexuality (2004)













